Tyre Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Built to Roll, Priced to Win

What is Tyre?
A tyre is circular in shape and made of a combination of rubber materials that fit perfectly over a circular rim on a wheel, providing traction, load-carrying capabilities, shock absorption, and directional stability. As such, tyres are engineered materials composed of a combination of natural or synthetic materials. They are composed of a combination of materials such as rubber, a combination of materials such as steel or textile, and various chemical materials, among others. Tyres have been engineered, among other functions, to provide road grip, carry weight, absorb friction, withstand heat, and resist exposure to various environmental factors. The contemporary version is available in various types that fit various characteristics of automobiles, making it a very important part of a mobility system.
Key Applications Across Industries:
The tyres find their application in a variety of transportation and industrial needs to serve as a medium between the vehicles and the ground surfaces. The automobile tyres help improve ride characteristics, braking, handling stability, and fuel efficiency during operation. It also helps improve tyre performances for all-season use, summer use, and for driving during winter conditions, etc., based on selected tread styles and-compounds of rubber material.
Tyres used in commercial vehicles such as trucks and buses are made for transporting heavy loads across long distances while at the same time ensuring durability and resistance to wear. Off the road tyres are used for construction vehicles, mining equipment, farming machinery, and forestry equipment. Tyres used for these applications are expected to perform in extreme conditions.
Another important role of tyres can be seen in two-wheelers like motorcycles, scooters, and bicycles, where they affect their stability and the safety of the rider. In aviation tyres, particular tyres designed for aircraft are designed to withstand maximum loads, temperatures, and braking forces during landing and takeoff operations. In industry, material handling equipment like forklifts and cranes use industrial tyres.
Other than that, tyres and their derivatives are used in motorsport, military, and recreational equipment. The sheer volume of equipment using tyres demonstrates how tyres are an integral component in ensuring movement, safety, and efficiency in a wide range of applications.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global tyre market reached a value of USD 181.11 Billion in 2025. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 273.82 Billion by 2034, at a projected CAGR of 4.7% during 2026-2034.
The tyre industry works on the back of persistent demand and growth in the global market with increasing numbers of vehicles, transportation activities, and industrial operations. The rise in the population of cities and elevations in income levels in different nations contribute to the increase in the demand for other vehicles like two-wheelers and cars; in other words, it generates demand for tyres as well.
Another factor that contributes to tyre consumption are infrastructure development, logistics, and the growth of e-commerce. With the flow of goods increasing, the need for reliable commercial vehicles also surges, thereby maintaining the consumption of commercial vehicle tyres like trucks and buses. This also contributes to the consumption of off-the-road tyres.
Replacement demand is another key market driving force, as tyres are eventually replaceable as they have a limited lifespan. Road conditions, driving habits, and climate changes force periodic replacement of tyres, which provides consistent market growth irrespective of new vehicle sales. Additionally, emphasis on road safety in terms of tyre tread depth, load indexes, and tire performance is a factor.
Technological advancements have shaped market dynamics in their way by bringing better performance, durability, and efficiency of tyres. Innovation within tread design, rubber compounds, and reinforcement materials improves fuel efficiency, minimizes rolling resistance, and improves safety - therefore, urging the end-consumer to upgrade. Besides, electric vehicle growth brings new performance needs, hence opening demand for specialized tyre designs.
The environmental and sustainability considerations also shape the market: a growing focus on recyclability, material efficiency, and circular economy practices influences product development and end-of-life management. Together, these structural, technological, and regulatory factors drive sustained global demand for tyres across transportation and industrial sectors.
Case Study on Cost Model of Tyre Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale tyre manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed tyre manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 2 million units of tyre annually.
Manufacturing Process: The process for manufacturing a tyre is a multi-step, highly engineered procedure focused on manufacturing tyres that are durable, efficient, and safe. The process starts from the raw material stage, where raw materials like natural rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, silica, oil, etc., are measured, uniformly mixed, and blended in an internal mixer for manufacturing various compounds. Each compound is formulated individually, viz., for the tread, sidewall, liner, etc.
The compounded rubber then undergoes further processing to make it a semi-finished component through processes called calendering and extrusion. Calendering helps shape rubber-coated fabric plies and steel belts, whereas extrusion is used to make components such as treads and sidewalls. The components are then cut into exact sizes for uniformity.
In the tyre building process, all elements of the tyre have to be mounted on a building drum. Here, a sequence is followed: the inner liner is placed first, and then the body plies, beads, belts, sidewalls, and tread. Up until this point of the process, the tyre, which is now a "green tyre," possesses no strength and no elasticity but has the correct tyre shape.
The green tyre then enters the vulcanization process; it gets molded in a special mold with heat and pressure applied to it. Vulcanization causes the different molecules in the rubber to bind chemically together, giving the tyre its strength properties and tread design.
Lastly, tyres are subject to inspection and quality tests, including visual inspection, X-ray inspection, uniformity tests, and balance tests. The tyres that meet the stipulated requirements are then labeled, stored, and distributed. The process ensures that tyres produced meet quality and safety standards.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
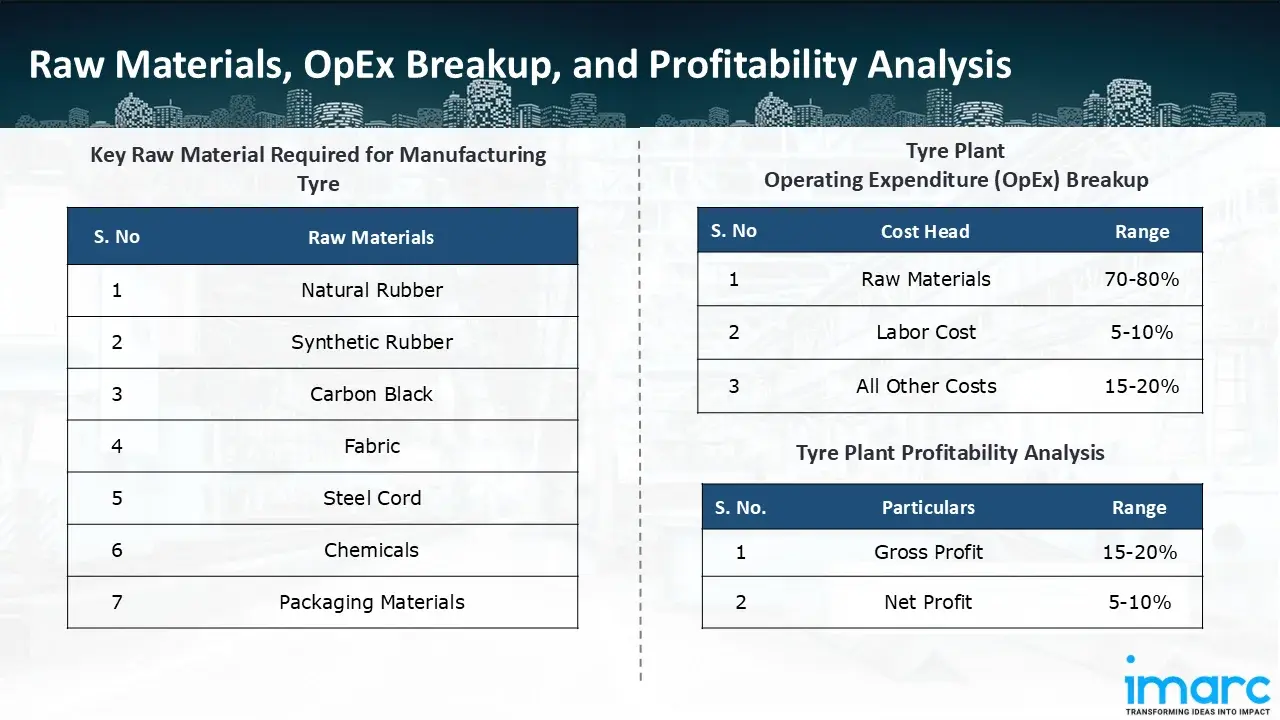
The basic raw materials required for tyre manufacturing include:
- Natural Rubber
- Synthetic Rubber
- Carbon Black
- Fabric
- Steel Cord
- Chemicals
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Mixing
- Calendaring
- Extruding
- Building
- Curing
- Finishing
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in tyre manufacturing plant ranges between 70-80%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 15-20%, and net profit lie between the range of 5-10% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the tyre manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 2 million units of tyre annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In February 2026, Apollo Tyres aims to address the increasing demand across vehicle tyre sectors by investing INR 5,810 crore to increase manufacturing capacity at its Andhra Pradesh factory. The investment will be financed by a combination of loans and internal accruals.
- In April 2025, Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company announced plans for a significant expansion of its Lawton, Oklahoma plant, the largest tire factory in its global network. The expansion intends to add 10 million units of premium tyre production capability annually, increasing the plant's production capacity by around 30%. The $320 million, four-year investment that includes this ambitious project aims to improve the plant's capacity to fulfil the increasing demand for larger rim-diameter tires, which are higher-profit and higher-margin products.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










