Ghee Manufacturing Cost Analysis: An Economic Assessment

What is Ghee?
Ghee is a class of clarified butter that, conventionally, is prepared by simmering butter until the milk solids separate and caramelize, leaving a golden, fragrant fat. Presently, it is widely used in South Asian, Middle Eastern, and increasingly global cuisines. Ghee has a high smoke point, long shelf life, and rich flavor, which makes it suitable for cooking, frying, and flavor enhancement. During its production, water and milk proteins are removed, making the product a lactose-free fat that contains fat-soluble vitamins and bioactive compounds. Its stability, purity, and distinctive taste make ghee an important culinary and functional ingredient in both traditional and modern food applications.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Ghee has a wide variety of uses in food, food service, nutraceutical, and seasoning applications Ghee has great versatility as a dairy product, finding immense applications in various culinary, medicinal, and industrial uses. It acts as a cooking medium, frying fat, and flavoring due to its high smoke point and rich aroma. Traditional uses of ghee include its application in the preparation of traditional dishes, sweets, bakery items, gravies, lentils, and rice preparations. In modern times, ghee finds its place in ready-to-eat meals, spreads, snack seasonings, bakery margarines, and gourmet products, presenting a natural alternative to hydrogenated fats and refined oils. Ghee, because of its digestive properties, has a wide applicability in the nutraceutical and wellness industry: ayurvedic formulations, herbal supplements, medicated ghee blends, and functional foods. It is believed to support nutrient absorption, joint lubrication, and gut health. The beauty and personal care industry uses ghee in creams, balms, lip products, and traditional skincare remedies due to its moisturizing and soothing properties.
Ghee is a value-added fat used in high-heat cooking and flavor enhancement, primarily in Indian, Middle Eastern, and fusion cuisines within the foodservice and hospitality industry. It is also used in confectionery, bakery items, and packaged foods, where stability and a long shelf life have made it appealing to food manufacturers. Overall, ghee's multifunctional nature, cultural significance, and adaptability across both traditional and modern product categories drive its widespread use.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global ghee market reached a value of USD 55.8 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 94.4 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 5.72% during 2025-2033. The driving factors for the global ghee market include dietary trends, cultural expansion, rising health consciousness, and growth in organized dairy processing. Arguably among the strongest is the global rise in demand for natural and minimally processed fats, as consumers increasingly steer away from hydrogenated oils and artificial additives. Ghee, being a pure dairy fat with no preservatives or emulsifiers, fits into the clean-label and whole-food trend. Its high smoke point, well above most vegetable oils, makes ghee a preferred fat for high-heat cooking in professional kitchens and health-conscious homes.
The rise of Ayurveda, yoga, and holistic wellness across international markets has contributed much toward the recognition of ghee as a functional food. With increasing promotion related to digestive health, nutrient absorption, and gut support, demand has risen significantly amongst health-conscious consumers and supplement brands. In regions with large diaspora populations such as the Middle East, North America, and Europe, cultural familiarity with ghee in everyday cooking has further expanded the market.
Another key driver is the rapid growth of the dairy industry, especially in the Indian subcontinent and South Asia, where a rise in incomes, urbanization, and a change in dietary pattern have increased consumption of value-added dairy products, including ghee. Modern retail channels, e-commerce platforms, and branded dairy companies have made ghee more accessible, shifting consumers from unregulated local products to standardized packaged varieties.
Other factors that further solidify the demand include the increasing use of ghee in food processing, ready-to-eat meals, gourmet products, and bakery applications. The introduction of value-added, premium, and artisan varieties includes A2 ghee, organic ghee, grass-fed ghee, and flavored ghee, which are creating newer product categories. Cumulatively, these trends reflect solid global growth based on nutrition awareness, cultural integration, and changing food preferences, placing ghee both as a traditional staple and as a modern functional ingredient.
Case Study on Cost Model of Ghee Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale ghee manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed ghee manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 1,500 tons of ghee annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process of ghee has a systematic heating, clarification, and separation sequence in order to retrieve pure clarified butterfat with a rich aroma and a long shelf life. The production starts with superior quality milk, which is first pasteurized and separated to produce cream. Churning of cream forms butter, which is the main raw material to manufacture ghee. This is further heated in large stainless-steel kettles or steam-jacketed vessels under controlled temperatures between 110°C to 120°C. As the butter melts, the water content starts to evaporate, and milk solids and proteins gradually separate from the fat. During heating, there is a stage when the mixture clarifies and the milk solids settle at the bottom, caramelize slightly, and provide the characteristic nutty aroma and golden color to ghee. At this moment, constant stirring has to be done in order to achieve even heating without burning. The separated and now clear and aromatic fat is carefully strained or decanted to remove residual solid impurities. On the industrial scale, centrifugation or filtration systems, including fine mesh filters or cloth filters, can be employed to effect high purity and clarity. After filtration, hot ghee is cooled gradually, during which its grainy texture develops—a desirable feature for many consumers. Cooled to the proper temperature, the ghee is packed into moisture-free airtight containers of metal, glass, or high-grade plastic in order to avoid oxidation and preserve flavor. During processing, quality control checks include monitoring moisture content, free fatty acids, aroma, and microbial safety. The careful process ensures the final product is shelf-stable, flavorful, and within food safety norms, making ghee acceptable in culinary, industrial, and nutraceutical applications.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for ghee manufacturing include:
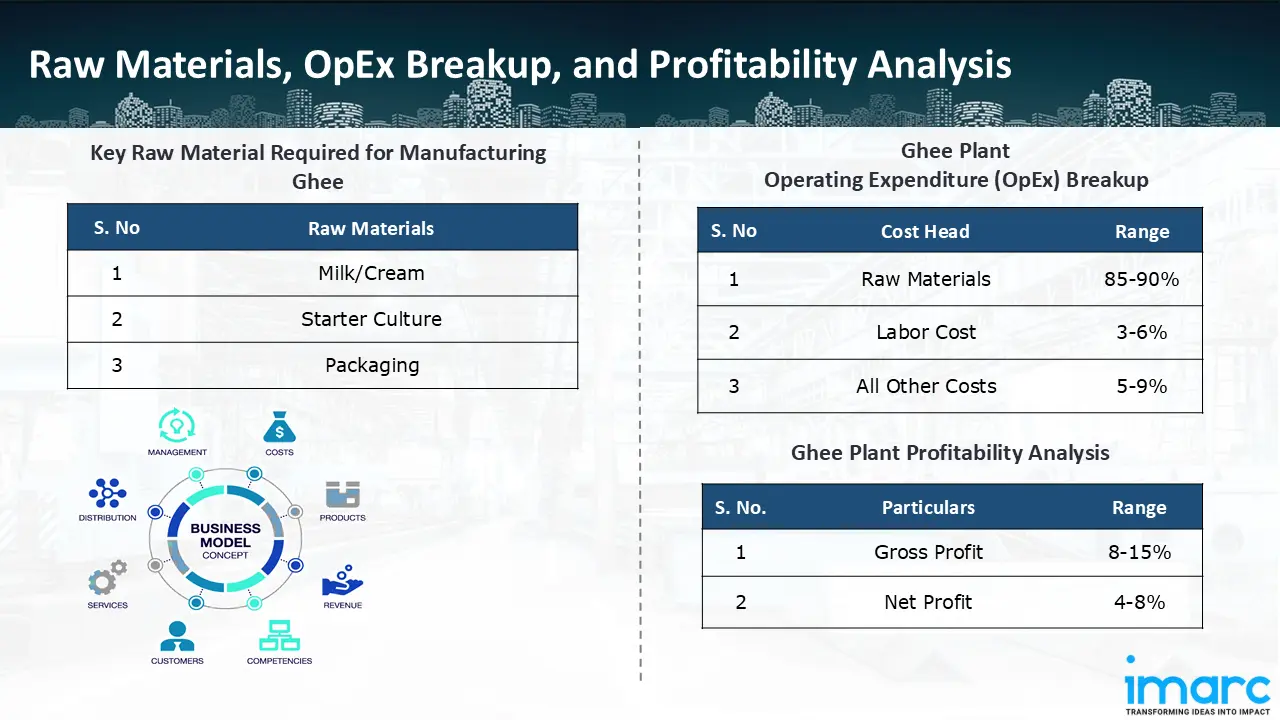
- Milk/Cream
- Starter Culture
- Packaging
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Pasteurization
- Cream Separation
- Boiling/Kettle
- Packaging
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in ghee manufacturing plant ranges between 85-90%, labor cost ranges between 3% to 6%, and all other costs ranges between 5-9% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 8-15%, and net profit lie between the range of 4-8% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the ghee manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 1,500 tons of ghee annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2025, FSSAI launched a month-long ghee purity testing drive across Madhya Pradesh, targeting both branded and loose ghee. Samples were sent to CES Bhopal and Choksi Indore labs. This move strengthened consumer confidence and pressured brands to maintain quality standards during the festive season.
- In June 2025, Parag Milk Foods announced its plans to strategically invest Rs 400 crore over the next three to four years. Additionally, during the next three to four years, the company intends to increase the share of its modern businesses, Pride of Cows and Avvatar, from 4.7% to 20%.
- In March 2025, Amaya Milk Company launched ‘Havan Ghee,’ a 100% pure cow ghee crafted for religious rituals. Made weekly under Vedic guidelines, it addressed the shortage of authentic ghee for pujas, boosting demand in the niche religious segment and reinforcing trust in ritual-grade ghee.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










