How Big Will Be the India Cloud Computing Industry by 2033?

The process of digital transformation in India has become an extremely fast one in the last several years, and cloud computing has become a foundation of the revolution. The India cloud computing market is experiencing an unprecedented growth as organizations in various sectors come to the realization of the strategic value of cloud infrastructure. Startups to multinational organizations are shifting their load to the cloud to increase operational efficiency, increase the security of the data, and generate innovation. This in-depth discussion covers the present-day situation and the future trends of the cloud computing sector in India, covering the market size forecasts, the deployment pattern, the growth of infrastructure, and the competitive environment that will define the market to 2033.
Enterprises Moving Workloads to Cloud for Storage & Security: SaaS, Virtualization, and Cloud Data Backup Becoming Essential
The shift of the enterprise workloads to the cloud platforms is now a strategic requirement and not a technological choice. The Indian business is also becoming aware that cloud computing has radical advantages that extend past cost reduction; it is scalable and flexible, and its security roles and capabilities are unmatched by conventional on-premise infrastructure.
The fastest-growing mode of cloud service in India is the Software as a Service (SaaS). Cloud-based customer relationship management, enterprise resource planning, human resources management, and collaboration tools are being used by organizations in different industries to replace legacy software systems. That transition will remove the necessity to invest in significant initial capital expenditures on software licenses and hardware infrastructure, and guarantee the updates and maintenance.
Cloud adoption strategies have depended on the adoption of virtualization technologies. Virtualization helps organizations better utilize computing resources and optimize their use, minimize energy use, and enhance disaster recovery by decoupling the computing resources from their physical hardware. Indian based enterprises are using virtualization to build flexible and dynamically defined data centers that can provide computing power in real-time to meet business demands.
Cloud data backup and disaster recovery solutions have gained critical importance as cyber threats become more sophisticated and data regulations more stringent. The increasing frequency of ransomware attacks and data breaches has compelled organizations to implement robust cloud-based backup strategies. Cloud storage provides geographic redundancy, automated backup schedules, and rapid recovery capabilities that significantly reduce downtime and data loss risks.
The Information Technology Act, 2000, and subsequent amendments have established a legal framework for electronic governance and digital transactions in India, providing regulatory clarity that encourages cloud adoption. Additionally, data localization requirements have prompted both global and domestic cloud service providers to establish infrastructure within India, addressing concerns about data sovereignty and compliance.
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst for cloud migration, forcing organizations to rapidly enable remote work capabilities. This experience demonstrated the agility and resilience that cloud infrastructure provides during disruptions, permanently changing enterprise attitudes toward cloud computing. Even as offices reopened, many organizations maintained hybrid work models supported by cloud-based collaboration and productivity tools.
Market Size & Growth Opportunity: Strong Adoption from IT, BFSI, Telecom, Retail and Government Projects
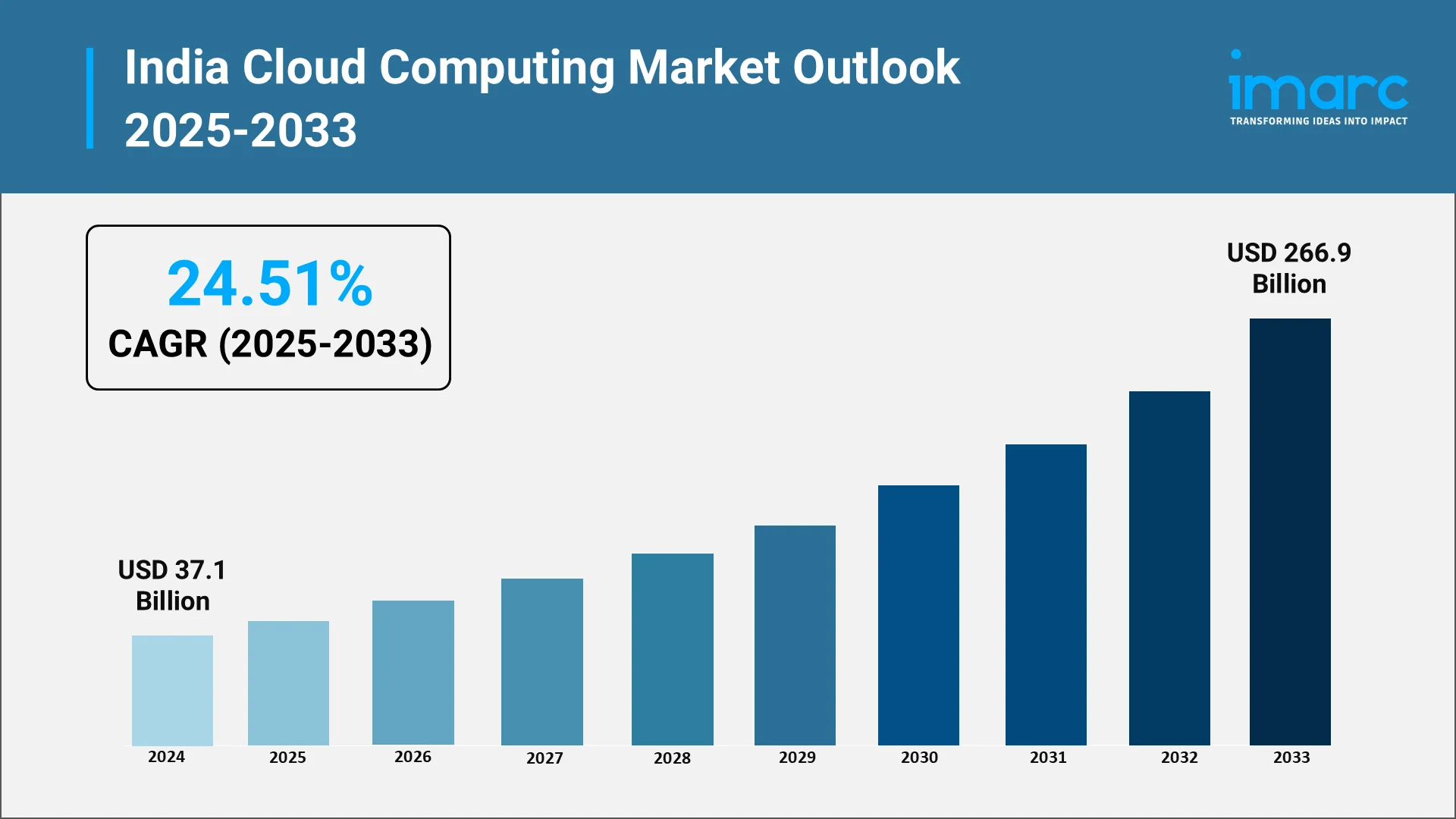
The India cloud computing market represents one of the most dynamic growth opportunities in the global technology sector. While specific market valuations from syndicated research firms are excluded per guidelines, the fundamental drivers and sectoral adoption patterns indicate substantial expansion potential through 2033. The India cloud computing market size reached USD 37.1 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 266.9 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 24.51% during 2026-2034.
The Information Technology (IT) sector leads cloud adoption in India, with software development companies, IT services providers, and technology startups leveraging cloud infrastructure for application development, testing, and deployment. Cloud platforms enable these organizations to scale computing resources dynamically, reducing time-to-market for new products and services while optimizing infrastructure costs.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) represents another critical growth segment. The Reserve Bank of India has been progressively developing frameworks for cloud adoption in the financial sector, recognizing the need for financial institutions to leverage cloud technologies while maintaining stringent security and compliance standards. Banks are migrating core banking systems, implementing cloud-based analytics for fraud detection, and deploying digital banking platforms that rely on cloud infrastructure.
The telecommunications sector is experiencing transformative change as operators deploy 5G networks and virtualized infrastructure. Cloud-native architectures enable telecom companies to offer network slicing, edge computing capabilities, and innovative services that traditional infrastructure cannot support. The convergence of telecommunications and cloud computing is creating new business models and revenue streams.
Retail and e-commerce organizations have become significant cloud computing adopters, driven by the need to manage fluctuating demand, personalize customer experiences, and compete effectively in digital marketplaces. Cloud platforms provide the scalability required to handle peak shopping periods while enabling advanced analytics, inventory management, and omnichannel customer engagement strategies.
Government digital transformation initiatives represent a massive growth opportunity for cloud computing in India. The MeitY (Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology) has established the MeghRaj Cloud Initiative to accelerate cloud adoption across government departments and facilitate the delivery of e-governance services. State governments are increasingly leveraging cloud platforms for citizen services, land records digitization, healthcare systems, and educational platforms.
Healthcare organizations are adopting cloud computing to implement electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, and medical imaging systems. The pandemic accelerated digital health adoption, with cloud infrastructure enabling remote consultations, health monitoring, and vaccine management systems.
Manufacturing enterprises are implementing cloud-based Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms, supply chain management systems, and predictive maintenance solutions. Cloud computing enables manufacturers to collect and analyze massive volumes of sensor data, optimize production processes, and implement Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Hybrid Cloud Emerging as the Most Preferred Deployment Model: Mix of Public + Private Cloud Improving Security & Cost Efficiency
The evolution of cloud deployment models reflects the maturing understanding of enterprise requirements in India. While public cloud adoption initially dominated the market, organizations are increasingly recognizing that hybrid cloud architectures offer optimal balance between flexibility, security, and cost efficiency.
Hybrid cloud deployments combine public cloud services with private cloud infrastructure and on-premises systems, allowing organizations to strategically place workloads based on specific requirements. Sensitive data and mission-critical applications can remain in private environments or on-premises infrastructure, while less sensitive workloads leverage the scalability and cost advantages of public cloud platforms.
Security considerations drive significant hybrid cloud adoption in India. Organizations in regulated industries such as banking, healthcare, and government must comply with data protection regulations and maintain control over sensitive information. Hybrid architectures enable these organizations to meet compliance requirements while still benefiting from cloud technologies for appropriate workloads.
Cost optimization represents another compelling advantage of hybrid cloud strategies. Organizations can maintain baseline infrastructure for predictable workloads while leveraging public cloud resources for variable demand, development and testing environments, or temporary projects. This approach eliminates the need to over-provision on-premises infrastructure while providing flexibility to scale when needed.
Multi-cloud strategies are becoming increasingly common within the broader hybrid cloud context. Rather than depending on a single cloud provider, organizations are distributing workloads across multiple public cloud platforms to avoid vendor lock-in, leverage best-of-breed services, and improve resilience. This approach requires sophisticated cloud management capabilities but offers significant strategic advantages.
Edge computing integration with hybrid cloud architectures is gaining traction, particularly in industries requiring low-latency processing such as manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality applications. Organizations are deploying edge computing nodes for real-time data processing while using cloud infrastructure for centralized analytics and long-term storage.
The technological maturity of hybrid cloud management platforms has significantly improved, reducing the complexity historically associated with multi-environment deployments. Container technologies like Kubernetes provide consistent application deployment across different infrastructure environments, while cloud management platforms offer unified visibility and control.
Indian enterprises are developing sophisticated cloud governance frameworks that define which workloads belong in different environments based on security requirements, compliance obligations, performance needs, and cost considerations. These frameworks enable organizations to maximize cloud benefits while managing risks effectively.
Major Data Center Expansion Across India: Global & Indian Players Setting Up Centers in Mumbai, Hyderabad & Chennai
Infrastructure development represents a critical enabler of cloud computing growth in India. The past several years have witnessed remarkable data center expansion across major Indian cities, driven by both global hyperscale cloud providers and domestic infrastructure companies.
Mumbai has emerged as India's primary data center hub, accounting for a substantial portion of the country's data center capacity. The city's position as India's financial capital, combined with excellent international connectivity through submarine cable systems, makes it the preferred location for financial services, e-commerce, and enterprise cloud deployments. Multiple submarine cables landing in Mumbai provide low-latency connectivity to international markets, which is essential for global businesses operating in India.
Hyderabad has become a major data center destination, attracting significant investments from both global cloud providers and Indian infrastructure companies. The city offers advantages including reliable power supply, availability of technical talent from the region's thriving IT industry, and supportive state government policies that facilitate infrastructure development.
Chennai represents another critical data center market, benefiting from its proximity to submarine cable landing stations and established position as a technology hub. The city serves as an important connectivity point for traffic between India and Southeast Asia, making it strategically valuable for organizations with regional operations.
Delhi-NCR (National Capital Region) continues to expand as a data center market, driven by government cloud initiatives, enterprise demand, and the concentration of corporate headquarters in the region. The presence of government agencies and public sector enterprises creates consistent demand for data center services with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Bangalore, as India's technology capital, hosts substantial data center capacity serving the IT services industry, startups, and research organizations. The city's concentration of technology talent and innovation ecosystem makes it attractive for cloud service providers targeting the technology sector.
Global hyperscale cloud providers have made substantial commitments to Indian infrastructure. These investments include not only data center facilities but also investments in renewable energy, local technology partnerships, and training programs to develop cloud skills among Indian IT professionals.
Indian infrastructure companies have also significantly expanded data center capacity, recognizing the strategic importance of digital infrastructure for national economic development. These domestic players bring deep understanding of local market requirements, regulatory environment, and connectivity needs.
The Digital India initiative has provided policy support for data center development, recognizing digital infrastructure as essential for the country's economic transformation. State governments compete to attract data center investments through incentives including land allocation, power subsidies, and streamlined approval processes.
Sustainability has become an increasingly important consideration in data center development. Operators are implementing renewable energy procurement strategies, advanced cooling technologies, and water conservation measures to reduce environmental impact. India's abundant solar energy potential provides opportunities for data centers to operate on clean energy.
Network infrastructure development complements data center expansion. Investments in fiber optic networks, internet exchange points, and content delivery networks improve connectivity between data centers and end users, reducing latency and improving application performance.
Top Companies in India Cloud Computing Market: AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Tata Communications, Reliance Jio
The competitive landscape of India's cloud computing market reflects a dynamic mix of global technology giants and domestic players, each bringing distinct capabilities and strategic approaches.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) maintains a leading position in India's cloud computing market through its comprehensive service portfolio, global infrastructure, and continuous innovation. AWS operates multiple availability zones in India, providing enterprises with geographic redundancy and low-latency access to cloud services. The company has invested heavily in local partnerships, developer training programs, and industry-specific solutions tailored for Indian market requirements.
Microsoft Azure represents a formidable competitor with particular strength in hybrid cloud deployments and enterprise software integration. Azure's seamless integration with Microsoft's productivity and business applications provides significant advantages for organizations already using Microsoft technologies. The company's commitment to Indian infrastructure includes multiple data center regions and partnerships with local systems integrators.
Google Cloud Platform brings differentiated capabilities in data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to the Indian market. Google's strengths in containerization technologies and open-source software appeal to technology-forward organizations and startups. The company has established a significant presence in India through infrastructure investments and partnerships with educational institutions.
Tata Communications represents a significant Indian player in the cloud computing market, offering infrastructure as a service, managed cloud services, and connectivity solutions. The company's global network infrastructure and deep understanding of Indian market requirements position it strongly for enterprise customers, particularly those with international operations requiring connectivity between India and other markets.
Reliance Jio has emerged as a potentially transformative force in India's cloud computing landscape. Leveraging its telecommunications infrastructure and market reach, Jio is developing cloud services targeting Indian enterprises and small businesses. The company's strategy includes edge computing capabilities, integration with its telecommunications services, and aggressive pricing models.
The competitive dynamics extend beyond these major players to include specialized providers focusing on specific segments such as infrastructure as a service, disaster recovery services, or industry-specific cloud solutions. Regional players and telecommunications companies are also entering the market, recognizing cloud computing as a strategic growth opportunity.
Partnerships and ecosystem development play crucial roles in the competitive landscape. Cloud providers collaborate with systems integrators, independent software vendors, and technology partners to deliver complete solutions addressing customer requirements. These ecosystems enable cloud providers to extend their reach and capabilities beyond core infrastructure services.
Competition in the Indian market increasingly focuses on factors beyond basic infrastructure provision. Organizations evaluate cloud providers based on criteria including data residency capabilities, compliance certifications, industry expertise, analytics and artificial intelligence services, and total cost of ownership rather than simply raw computing power or storage capacity.
Conclusion:
The India cloud computing industry stands at an inflection point, with robust growth trajectories extending through 2033, driven by digital transformation imperatives, regulatory support, infrastructure development, and increasingly sophisticated enterprise adoption strategies. The convergence of hybrid cloud architectures, edge computing capabilities, and artificial intelligence services will define the next phase of market evolution.
Organizations that strategically leverage cloud computing will gain a competitive advantage through improved agility, enhanced security, data-driven decision-making, and the ability to rapidly deploy innovative services. The substantial infrastructure investments by both global and domestic players demonstrate strong confidence in India's long-term cloud computing potential.
As India continues its journey toward becoming a digital economy, cloud computing will serve as essential infrastructure enabling innovation across industries, supporting government digital initiatives, and positioning Indian enterprises to compete effectively in global markets. The question is no longer whether to adopt cloud computing, but rather how to maximize its strategic value through thoughtful architecture decisions, governance frameworks, and continuous capability development.
Choose IMARC Group As We Offer Unmatched Expertise and Core Services
- Data-Driven Market Research: Enhance your understanding of India's cloud computing landscape, including adoption patterns across IT, BFSI, telecom, retail, and government sectors, through comprehensive market research reports covering deployment models, infrastructure trends, and competitive dynamics.
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Anticipate emerging developments in cloud technologies, from hybrid and multi-cloud architectures to edge computing integration and AI-powered cloud services, with detailed projections across key industry verticals and geographic regions.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Analyze the competitive positioning of global hyperscale providers and Indian infrastructure players, evaluate service portfolios, assess pricing strategies, and monitor technological innovations shaping the cloud computing ecosystem.
- Policy and Infrastructure Advisory: Navigate India's evolving regulatory framework for cloud computing, including data localization requirements, security standards, and government initiatives like MeghRaj, while tracking infrastructure development across major data center markets.
- Custom Reports and Consulting: Access tailored insights aligned with your organizational objectives, whether evaluating cloud migration strategies, assessing market entry opportunities, selecting optimal deployment models, or developing go-to-market strategy for cloud-based solutions.
At IMARC Group, we empower technology leaders, investors, and enterprises with the intelligence and clarity required to succeed in India's rapidly evolving cloud computing landscape. Partner with us to transform data into strategic advantage, because informed decisions drive sustainable growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










