French Fries Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Turning Potatoes into Profits

What are French Fries?
French fries are thin strips of baked or deep-fried potatoes with a fluffy inside and a crispy outside. They originated in Europe and are now a common fast-food staple that is consumed as a snack or side dish in many countries. French fries are made mostly from high-starch potatoes and are produced in large quantities by chopping, blanching, frying, and occasionally freezing. They are among the most well-liked and extensively consumed potato-based food products in the world because of their ability to be seasoned, flavored, or combined with condiments like cheese, mayonnaise, or ketchup.
Key Applications Across Industries:
French fries have significant culinary and commercial applications in various segments of the food industry. They are a core offering in quick-service restaurants, cafes, and fast-casual dining chains, mainly as side dishes to burgers, sandwiches, fried chicken, or grilled meats. In home cooking, frozen French fries are convenient ready-to-cook versions that require negligible preparation time, with consistent taste and texture. Above and beyond the traditional salted variety, French fries also come in seasoned, spiced, or flavored variations, catering to different regional tastes, such as peri-peri, masala, truffle, or cheese-loaded. In the snack and catering business, French fries are also served as appetizers, finger foods, or as part of combo meals, enjoyed both by kids and adults. They find their applications in institutional catering, too, like schools, hospitals, and airlines, where frozen standardized French fries ensure quality and portion control. Food manufacturers make use of similar processing techniques to obtain derivative products like potato wedges, curly fries, and hash browns. With the increasing trend for healthier diets, air-fried and baked versions have also gained momentum in the retail and health-food sectors. French fries, therefore, combine versatility, affordability, and adaptability, making them an indispensable constituent of global culinary culture and commercial foodservice operations.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global French fries market reached a value of USD 17.12 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 27.56 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 5.4% during 2025-2033. The global market for French fries is driven by a blend of lifestyle shifts, food service expansion, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Among these factors, the rapid growth of QSRs and fast-casual dining chains, where French fries are almost a necessity as a side dish, has become one of the major driving forces. As urbanization around the world intensifies, with an increased demand for convenient, ready-to-consume, and reasonably priced food, French fries fall perfectly within the quick-meal phenomenon. Increasing disposable incomes and busy consumer work life have furthered the preference for frozen and pre-cooked fries due to their consistent taste and very minimal preparation time.
Improvements in the technology of freezing, oil management, and quality control have assisted manufacturers in maintaining the sensory characteristics of freshly made fries even after long storage, which has widened the export potential and international trade. The extension of cold-chain logistics further enabled producing companies to supply frozen French fries to international markets, especially in countries where access to fresh potatoes is difficult. Moreover, the rise of food ordering platforms through the internet and the increase in popularity of Western-style fast food in developing economies have created a continuous demand for the product.
The health-conscious and plant-based eating habits of consumers are influencing the development of air-fried, reduced-sodium, and non-oil variants of their food. In parallel, value addition also takes place through flavoring and packaging innovations such as spiced, crinkle-cut, or loaded fries. This extends their market reach beyond traditional QSR outlets into retail and household consumption. All in all, a combination of convenience, taste appeal, and global lifestyle transformation underlines the momentum of the market, guaranteeing that French fries will maintain their leading position and grow as an adaptable product in the global frozen and snack food market.
Case Study on Cost Model of French Fries Manufacturing Plant
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale French fries manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed French fries manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 2,500 tons of French fries annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process of French fries is a well-engineered series of steps that ensures consistency, texture, and quality at both industrial and commercial levels. Manufacturing starts with the raw potato selection process, where high-starch, low-sugar varieties, like Russet Burbank or Innovator, are used for crispy outside and fluffy interiors. First, the potatoes are washed and then peeled by either abrasive peelers or steam peelers to remove skin without compromising the flesh. Following peeling, they are trimmed and sorted to eliminate defective tubers or those with greenish colors that may hamper flavor or appearance.
Next, the potatoes are cut into uniform strips using precision cutters or blades to achieve specific dimensions, usually 7–10 mm for standard fries. Immediately after cutting, the potatoes are washed in cold water to remove excess surface starch, which helps prevent clumping and assure a crisp product at the end. They then undergo a blanching process: partial cooking in hot water or steam for a short period is carried out to inactivate the enzymes, preserve color, and give the desired internal texture to the fries. After blanching, the fries are surface-dried with hot air to take off excess moisture just before frying. The process involves par-frying the potatoes in vegetable oil at controlled temperatures, usually around 170-180°C, so that a golden crust forms while still retaining an interior softness. Par-fried, they are then blast frozen or cryogenically frozen to preserve freshness and texture, before being hygienically packed and cold-chain stored until distribution. This whole automated process ensures that batches of French fries have consistent taste, color, and crunch-each time the same quality product, whether served in a restaurant or home-prepared.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
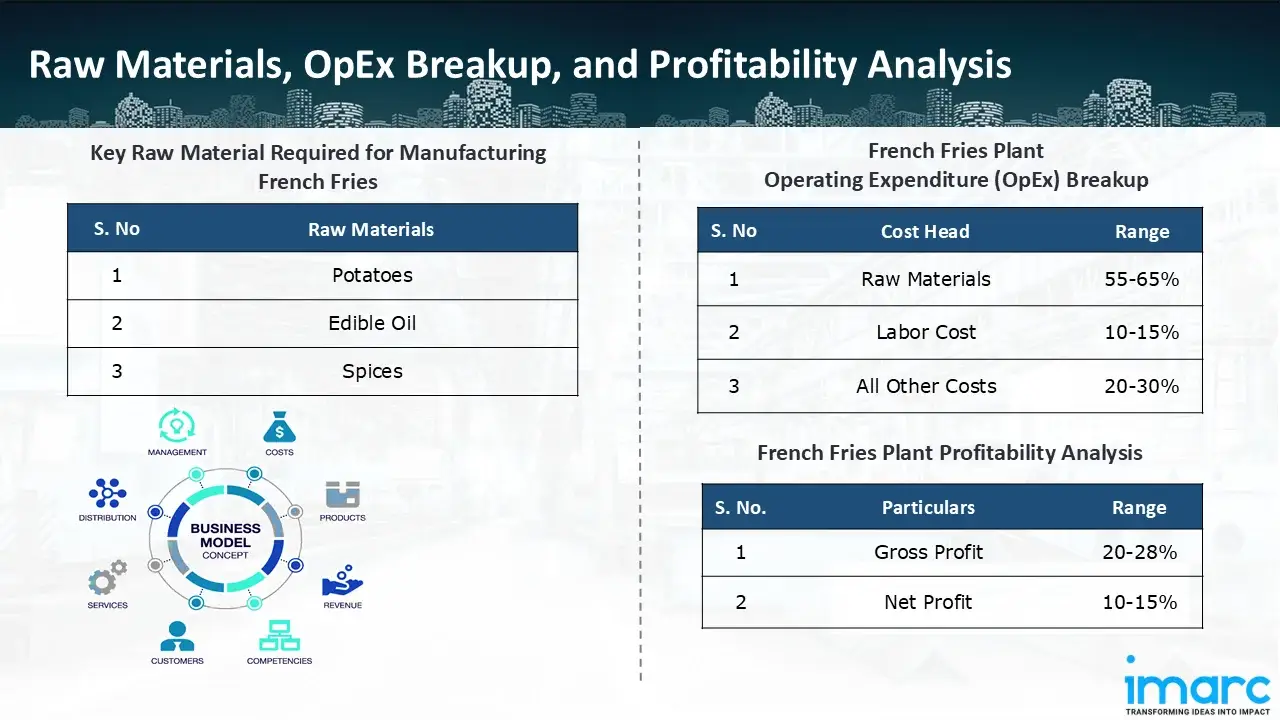
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for French fries manufacturing include:
- Potatoes
- Edible Oil
- Spices
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Washing & Peeling
- Cutting
- Blanching
- Frying/Freezing
- Packaging
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in French fries manufacturing plant ranges between 55-65%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 20-30% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 20-28%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the French fries manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 2,500 tons of French fries annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In October 2025, the official opening of Lamb Weston Holdings, Inc.'s 40,000-square-meter production facility in Mar del Plata, Argentina's Buenos Aires region, was announced by the company, which is a major global supplier of frozen potato products.
- In May 2025, Falcon Agrifriz Foods Private Limited opened a cutting-edge, completely automated factory to produce frozen potato products in Mehsana, Gujarat. According to the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that Falcon Group and the Gujarati government signed, this cutting-edge facility represents a major turning point. In an effort to make Gujarat a global centre for frozen potato-based goods, the group has invested about Rs1,050 crore in the state.
- In January 2025, Allana Consumer Products Ltd announced its plan to invest Rs 300 crore to establish new manufacturing facilities in Gujarat and North India by 2027. This expansion into the French fries and frozen potatoes market plans to capture a minimum of 3% global market share by 2029, leveraging their infrastructure and market reach in the convenience food sector.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











