Polyester Fabric Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Synthetic Threads, Real Returns

What is Polyester Fabric?
Polyester fabric is a type of synthetic fabric made from polyester fibers. The main source of polyester fibers is petrochemical polymers like polyethylene terephthalate. Polyester fabric is made from processing chips of polymers to produce continuous filaments and staple fibers. The processing of polymers involves heating and melting chips of polymers made from petrochemical materials to produce continuous filaments and staple fibers. The fibers are then woven and knitted to produce fabric. Polyester fabric has desirable properties of high tensile strength, dimensional stability, wrinkle and shrinkage resistance, and low moisture absorption. Polyester fabric can be made in various textures and has different properties.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Polyester fabric finds many applications in clothing, home textiles, industrial articles, and technical textiles. Polyester is used to manufacture casual wear, sportswear, activewear clothing, outerwear clothing, uniform clothing, and fashion clothing. Polyester possesses good shape recovery properties and is wrinkle resistant and can withstand multiple washing cycles. As polyester is prone to creasing and wear-and-tear, many times it is mixed with natural fibers like cotton or wool to add strength and longevity to the fabric. Polyester possesses high resistance to heat and can withstand high temperatures.
In the home textile industry, polyester fabrics are processed to be used in curtains, upholstery, bedding, cushions, carpets, or rugs. The colorfastness and resistance to fading properties make the polyester fabrics suitable for use in situations where sunlight affects their appearance. The hotel industry uses polyester fabrics extensively to make hotel furnishings, curtains, or bedding.
Applications in industry and technology are an important use type. Polyester fabric is employed in manufacture of conveyor belts, safety belts, ropes, geotextiles, filter, and insulation materials owing to its tensile strength and chemical resistance. Polyester fabric is also employed in making car interiors in seats, headliners, and trims. Besides this, its applications in manufacture of soft, hygiene, and medical textiles, and packaging materials are quite prominent. Polyester fabric is quite flexible in manufacture and therefore is employed for its utility and aesthetic appeals in different sectors.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global polyester fabric market reached a value of USD 110.2 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 227.2 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 8.4% during 2025-2033. The driving forces behind the global polyester fabric market are a combination of cost-effectiveness, benefit, growing industries, and consumer preferences. One of the key factors responsible for the growing preference for polyester is the need for an economical alternative compared to other natural fabrics. It is less expensive than many other natural fabrics yet supplies the same quality.
There is prominent growth presence of textile and fast fashion. This supports the demand for polyester fabric. Polyester is favored by manufacturers due to ease of production processing, colors, and automation properties. There is also steady growth due to sport wear or active wear. Polyester fabric is supported by properties like moisture-wicking functionality, lightness, and strength.
Urbanization as well as rising disposable income in emerging economies drive demand for home furnishings, interior textiles, and automotive interiors, all of which have a high use of polyester fabrics. Infrastructure development, combined with increasing industrialization, further improve demand for technical textiles, where the ability of polyester fabrics to withstand various environmental factors becomes a main advantage.
Sustainability trends are also impacting the market. Improvements in the production of recycled polyester using post-consumer plastic waste have increased the sustainability of polyester fibers. This is in line with the sustainability commitments of brands as well as the need for reduced plastic waste.
Technological innovation contributes further to growth because of the ability the technology posits for functional improvements such as breathability, softness, flame retardancy, and antimicrobial functionality. This flexibility that polyester has because of technological innovation enables the material to meet different performance needs. It is therefore the cumulative effect of affordability, scalability, performance advantage, sustainability initiatives, and growing applications that influences the worldwide demand for the manufacturing of polyester fabric.
Case Study on Cost Model of Polyester Fabric Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale polyester fabric manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed polyester fabric manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 8 million meters of polyester fabric annually.
Manufacturing Process: The process of making polyester fabric entails a series of operations that range from the production of polyester, fiber production, yarn production, to fabric production. The production process begins with the formation of polyester chips through the chemical reaction of purified raw materials. The polyester chips are then cooled, solidified, and dried in order to eliminate any moisture which may be present. The dried polyester chips are then melted and extruded through spinnerets in an operation referred to as melt spinning. The melted polyester is cooled instantly through the spinnerets to form polyester fibers. The newly produced filaments are drawn and extended to align the polymer molecules, which enhances tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to contraction. Depending on their use, the filaments are either utilized directly in their filament form, known as filament yarn, or converted to staple fibers of predetermined lengths. The staple fibers are processed through spinning techniques to get similar yarns like those obtained from natural fibers. These are then woven or knitted into fabrics using suitable textile processing machinery depending on the intended type of fabric. Subsequent finishing operations can be performed on these fabrics to improve functionality and aesthetics. These may involve heat setting for size stabilization, dyeing and printing for creating colors and designs, or chemical finishing to confer effects such as water management, wrinkle resistance, flame resistance, and softness. Quality control checks are done throughout the production process to ensure consistency of fiber strength, weight, colorfastness, and other performance-related characteristics. Finished polyester is sampled, rolled, and packaged for distribution. Modern production techniques are increasingly focused on energy efficiency, recycling, and automation in a continuing effort to make production “greener” and more productive.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
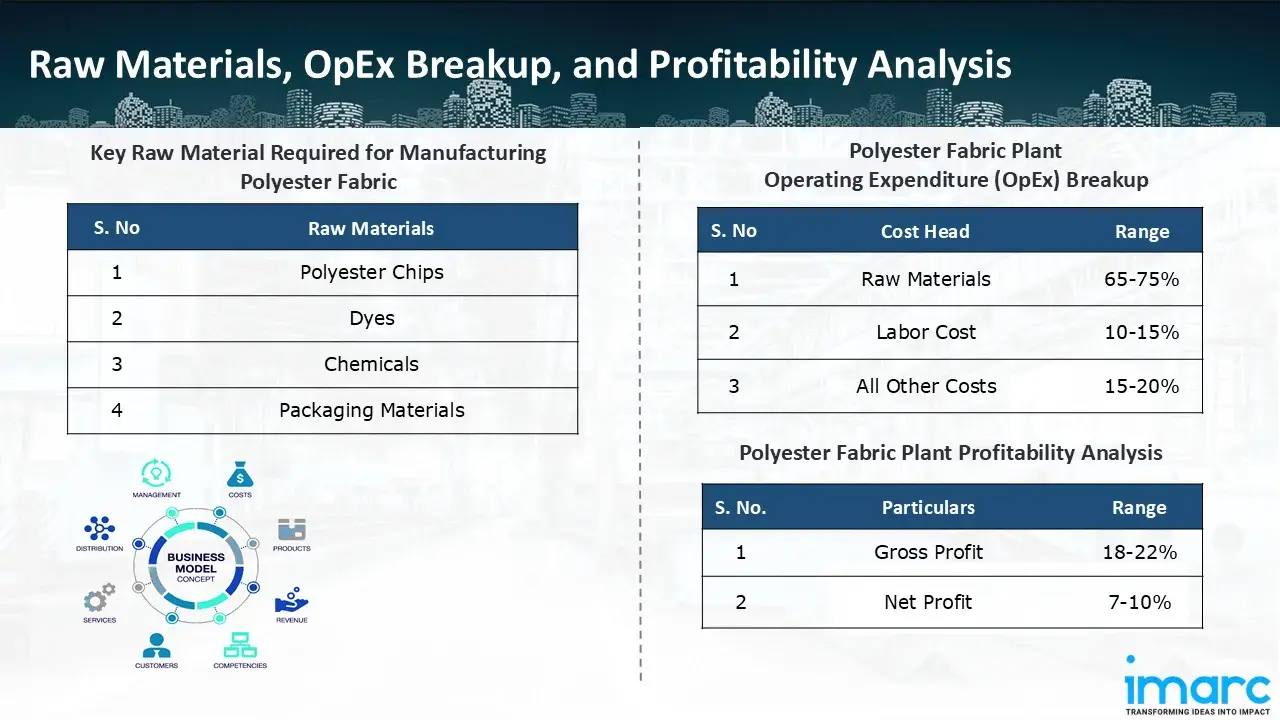
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for polyester fabric manufacturing include:
- Polyester Chips
- Dyes
- Chemicals
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Spinning
- Texturizing
- Weaving/Knitting
- Dyeing
- Printing
- Finishing
- Quality Control
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in polyester fabric manufacturing plant ranges between 65-75%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 18-22%, and net profit lie between the range of 7-10% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the polyester fabric manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 8 million meters of polyester fabric annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In September 2025, Ester Loop Infinite Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (ELITe), a 50:50 joint venture between Loop Industries of Canada and Ester Industries Limited, stated that Taro Plast S.p.A. of Italy announced getting supplies from its planned Infinite LoopTM production facility in Gujarat. Additionally, Loop Industries and Hyosung TNC of South Korea have formed a strategic partnership to assist international brands in switching to circular polyester.
- In June 2025, Syre, a textile recycling company supported by H&M, announced that it would supply recycled polyester to U.S. retailers Gap (GAP.N) and Target (TGT.N) as demand for sustainable fashion increases.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











