Meat Processing Cost Analysis: Cost Drivers & Efficiency Insights

What is Meat?
Meat generally denotes the animal tissues that are consumed and mainly include muscle fibers, though the content of fat, connective tissue, and moisture may vary. There are a number of sources, although they are mainly livestock such as cattle, pigs, sheep, poultry, and, in some regions, game animals. Meat is valued for its high-quality protein, essential amino acids, vitamins-particularly B-complex-and minerals like iron and zinc. Its texture, flavor, and nutritional profile vary depending on species, cut, age, and processing methods. Meat plays an important role in global diets and forms the basis of numerous culinary traditions, food industries, and cultural practices.
Key Applications Across Industries:
There are a variety of ways meat is used in international cuisine because it is versatile, nutritious, and can be prepared in different ways. During household cooking, meats are usually roasted, grilled, fried, stewed, or boiled to make ordinary dishes in different parts of the world. Beefsteaks, chicken curries, roasted lamb, and pork chops all form vital dishes in many regions. Meat also forms the base for processed foods, such as sausages, bacon, ham, nuggets, patties, and deli slices, which are convenient and have longer shelf lives. These processed forms cater to the demands of modern lifestyles where speed and portability are major concerns.
Meat is a central ingredient in restaurants, fast-food chains, catering, and institutional kitchens. High-demand categories consistently include burgers, kebabs, shawarma, BBQ plates, and fried chicken. Value-added uses of meat also include marinated cuts, ready-to-cook meal kits, and seasoned frozen items, which are designed to make home cooking easier.
Beyond being consumed by humans, meat by-products play vital roles in pharmaceuticals, pet food, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics. Collagen, gelatin, enzymes, and fats resulting from meat processing have applications in the confectionery and capsule industry, skin care, and various industrial formulations. Moreover, meat features significantly in nutrition programs and humanitarian food aid due to its dense protein content. In summary, the uses of meat span widespread areas in culinary, commercial, industrial, and nutritional fields.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global meat market reached a value of USD 1.43 Trillion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 1.71 Trillion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 1.91% during 2025-2033. Demographic, economic, technological, and cultural factors combine to drive the global meat market. Some of the key drivers include population growth and increased demand for proteins in developing regions, where rising incomes improve the affordability and desirability of meat diets. The process of urbanization reinforces this, as city-based lifestyles encourage ready-to-eat and processed meat products for convenience.
Cultural acceptance and changing food habits shape demand. Meat consumption is linked to socializing in many cultures, marking festive occasions, celebrations, and being an integral component of food culture, which reinforces its presence in everyday diets. The growth of fast-food chains and restaurant culture worldwide also pushes up demand for poultry, beef, and value-added meats, especially among younger consumers. Technological advancements in cold-chain logistics, packaging, and processing have enhanced the global supply chains of meat, enabling producers to access even the most distant markets with extended shelf lives and better safety. Improvement in refrigerated storage and transportation has boosted the demand for frozen and chilled categories.
Another driver is the growth of value-added and processed meat segments, such as sausages, deli meats, and ready-to-cook marinated products. These are in tune with contemporary lifestyles that demand convenience but not at the cost of taste or protein intake. The growth in the importance of nutritional intake, especially protein-based diets touted by fitness and wellness programs, adds to the continued demand for poultry, lean cuts of meat, and high-protein meat snacks.
Other supportive factors to market expansion include global trade agreements, government support for the development of livestock, and improvements in animal genetics and feed efficiency, which all enhance productivity and reduce costs of production.
Case Study on Cost Model of Meat Processing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale meat processing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed meat processing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 3,000 tons of meat annually.
Processing Flow: The meat processing process is a systematic process that is intended to achieve safety, quality, and efficiency from slaughtering to the final products. It starts with animal selection and ante-mortem inspection, whereby veterinarians inspect the health and fitness of the animals for human consumption. Qualified animals then go through stunning, followed by slaughtering, according to regulated humane methods. Post-slaughter, bleeding is done without delay to maintain product quality, followed by evisceration: removal and inspection of internal organs for safety. The carcass is subsequently washed, trimmed, and chilled-usually in cold rooms or blast chillers-to retard the growth of microorganisms and to stabilize the muscle tissues. Chilling also affects the tenderness and color development of meat. Following sufficient chilling, carcasses are cut up and deboned into primal and sub-primal cuts, then portioned, graded, and packaged according to intended use. For processed meats, the process involves additional steps. Minced, emulsified, cured, marinated, or cooked-the way meat is prepared would depend on the type of product being manufactured. Some common ingredients that may be added to enhance flavor and texture include salt, spices, curing agents, and binders. Sausages and patties involve mixing, forming, stuffing, and sometimes smoking, cooking, or drying. Products like nuggets and patties need breading, battering, and frying or par-frying before freezing. In the process, hygiene, temperature control, and quality assurance are strictly followed. Packaging technologies used include vacuum sealing, MAP, and rapid freezing to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. Finally, the products are labeled, stored in cold chain conditions, and distributed to retail, foodservice, or export markets.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for meat processing include:
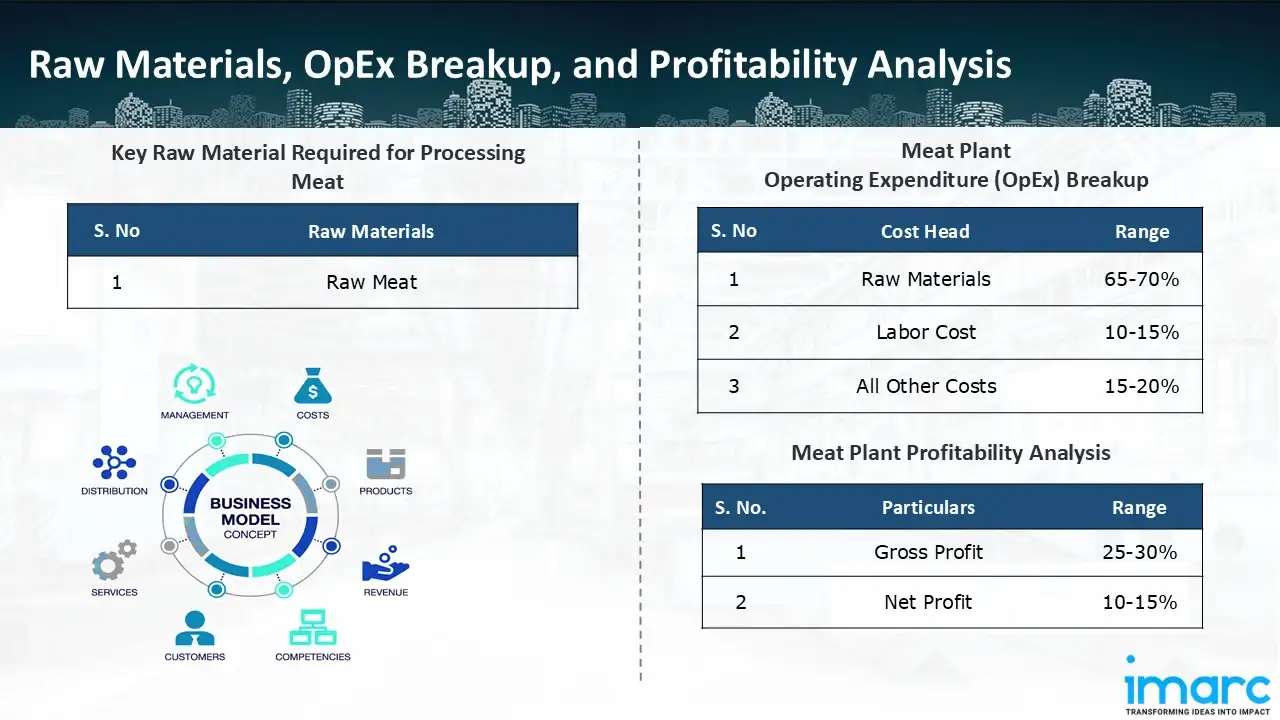
- Raw Meat
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Reception & Slaughter Section
- Evisceration & Cutting Section
- Preservation & Storage
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a processing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a processing plant effectively. OpEx in a processing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a processing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in meat processing plant ranges between 65-70%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 25-30%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the meat processing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, processing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of processing 3,000 tons of meat annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale processing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In October 2025, Avesterra Group, a Ukrainian corporation, opened a new meat processing facility in Volyn. With a capacity of 13,500 broilers per hour and an area of around 30,000 square meters, the facility has cost more than €60 million. The industrial site includes 11 growing farms, its own feed mill, and a modern processing plant.
- In June 2025, Walmart announced the grand launch of its first-ever owned and run case-ready beef factory in Olathe, Kansas. The opening marks Walmart's first-ever owned and operated, case-ready beef facility, offering quality beef to customers in the Midwest.
- In March 2025, JBS S.A., one of the largest meat packers in the world announced a US$100 million investment to construct two new facilities in Vietnam.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the processing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish processing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104











