Bamboo Plywood Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Breaking Down the Value Chain

What is Bamboo Plywood?
Bamboo plywood is an engineered wood product that is made by laminating thin strips or veneers of bamboo into multi-layered panels to create a stable, uniform sheet material combining the natural aesthetics of bamboo with the structural versatility of plywood.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Unlike conventional plywood made from hardwood or softwood veneers, bamboo plywood most often uses strand-woven, horizontal, or vertical lamination patterns of bamboo culm that are bonded under heat and pressure with formaldehyde-free or low-emission adhesives. Panels made from this material retain the characteristic linear grain and warm coloration of bamboo while offering enhanced dimensional stability, a reduced tendency to warp, and notable strength-to-weight properties. Workflows may include drying the bamboo to controlled moisture levels, slicing or slitting the culm into veneers or strands, carbonization or heat treatment to desired color tones, then reconstituting the material into cross-laminated layers to balance the mechanical properties. Finished bamboo plywood can be sanded, machined, veneered, or coated to meet architectural and furniture specifications; it is used in cabinetry, flooring underlayments, wall panels, furniture components, doors, and specialty millwork when designers seek out a renewable and visually distinctive alternative to tropical hardwoods. Besides aesthetic reasons, one of the reasons that bamboo panels are popular among manufacturers and specifiers is that they can be made in large, consistent sheet sizes, accept standard fasteners and finishes, and integrate easily with modern manufacturing techniques such as CNC machining and lamination. As an engineered product, bamboo plywood also allows control over density, stiffness, and thickness combinations, enabling tailored solutions for both structural and decorative applications and utilizing the rapid renewability of bamboo when compared to more slowly growing tree species.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global bamboo plywood market reached a value of USD 8.6 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 12.94 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 4.3% during 2025-2033. Converging factors driving global interest and adoption of bamboo plywood range from sustainability preferences to design trends, regulatory pressures, and industrial capability improvements. Sustainability considerations are perhaps the most significant catalyst: bamboo grows much faster than most timber species and, in many management systems, can be harvested without replanting, offering a renewable raw material profile that resonates with architects, manufacturers, and consumers seeking lower-impact alternatives to traditional hardwoods.
This environmental positioning is amplified by corporate and institutional procurement policies favoring certified, renewable, or rapidly regenerating materials, particularly for projects seeking to reduce embodied carbon and support circular economy goals. Design and aesthetic currents also propel demand: contemporary interiors and products often emphasize natural textures and linear grain patterns, and bamboo's distinctive look provides a premium, modern alternative that transfers well across furniture, flooring, and wall systems. On the technical and supply side, advances in processing technology and adhesive formulation increase the reliability and performance of engineered bamboo panels, with manufacturers now able to make consistent, larger-format sheets with predictable mechanical properties. Such production improvements reduce barriers for mainstream manufacturers to substitute bamboo panels into existing production lines. Regulatory and trade dynamics further bolster uptake in some regions: restrictions on logging or incentives for sustainable materials make bamboo plywood comparatively attractive, while building codes in various jurisdictions are increasingly open to engineered alternatives once product standards and certifications are met. Commercial drivers include growing demand from the furniture and fit-out industries, expansion in modular and prefabricated construction where lightweight, durable panels are valued, and interest from manufacturers seeking differentiation through eco-led branding. Lastly, social and rural development objectives in bamboo-growing countries encourage investment into plantation management and processing capacity, creating more reliable supply chains that in turn attract international downstream buyers-a virtuous cycle that continues to underpin the global momentum behind bamboo plywood.
Case Study on Cost Model of Bamboo Plywood Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale bamboo plywood manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed bamboo plywood manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 10,000 cubic meters of bamboo plywood annually.
Manufacturing Process: Bamboo plywood manufacturing consists of a series of well-controlled mechanical, chemical, and thermal operations that are intended to convert raw bamboo culms into standardized, high-strength panel sheets for industrial and decorative applications. It starts with the harvesting of matured bamboo culms, usually within 4–6 years, for optimal fiber strength and density. The culms are then cut into small sections and longitudinally split into thin strips or slats. These strips are de-noded, planed, and boiled or steamed to eliminate sugars, starch, and resins that attract pests or promote decay. Later, the bamboo is dried in controlled kilns to bring moisture content down to about 6–8% for dimensional stability during lamination. These strips are then carbonized or bleached to the desired color and finish before being glued together with low-formaldehyde or other eco-friendly resins like phenol-formaldehyde (for exterior-grade panels) or urea-formaldehyde (for interior applications). The glued strips are oriented either horizontally, vertically, or strand-woven to form a mat or layered stack depending on the intended grain orientation and strength properties required. These layers are also subjected to hot pressing under high temperature and pressure to ensure that the adhesive cures and bonds the bamboo into a solid panel. After pressing, these panels are trimmed, sanded, calibrated, and sometimes coated or laminated to attain smoothness and surface uniformity. The final quality check is made for uniformity in thickness, integrity of the surface, and bonding strength. The bamboo plywood made this way has excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for furniture, flooring, cabinetry, and architectural applications.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
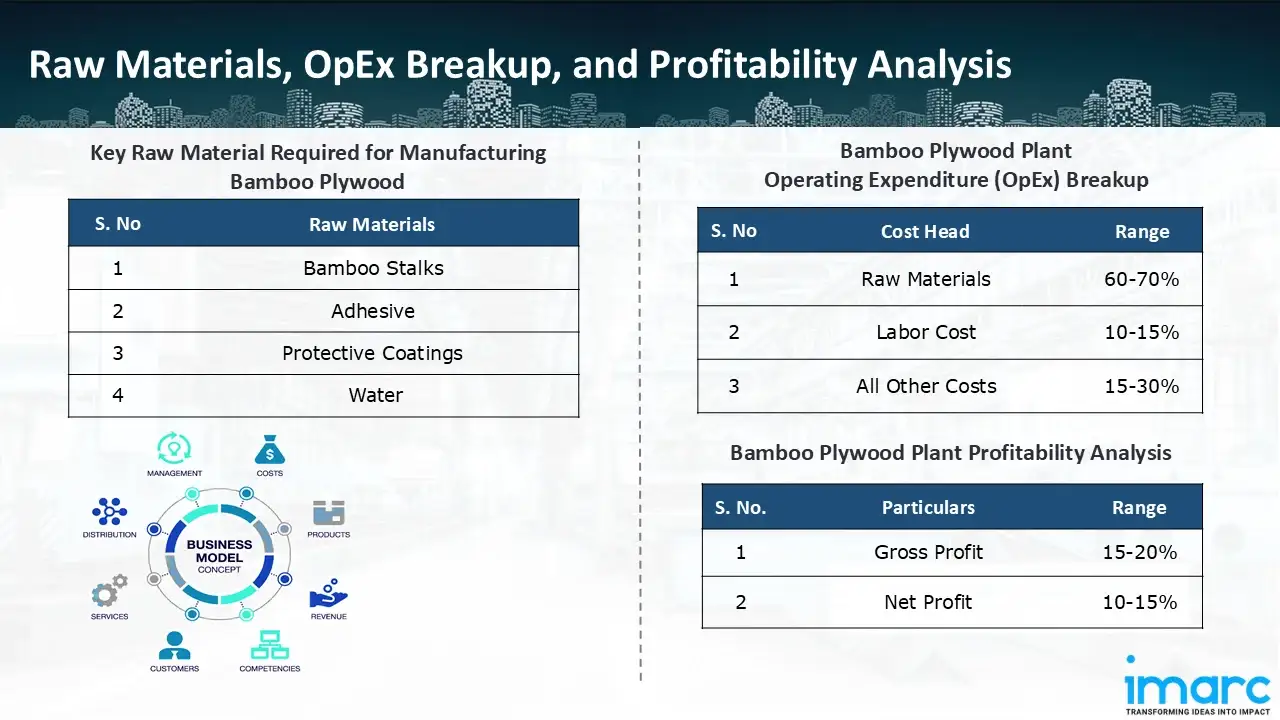
The basic raw materials required for bamboo plywood manufacturing include:
- Bamboo Stalks
- Adhesive
- Protective Coatings
- Water
Machineries Required:
- Conveyors / Forklifts / Log Handling Table / Hydraulic Log Loader
- Debarking Machine
- Decoring Machine / Plunger Decorer
- Straightening Machine / Internal-External Pressure Device
- Rotary Veneer Lathe / Slabbing Machine / Cutter (Slicing Machine)
- Boiling/Kettle / Continuous Steaming Units (Autoclave / Steam Chamber)
- Veneer Dryer / Continuous Dryer / Flash Dryer / Double-Drum / Conveyor Dryer
- Veneer Splicing/Jointer / Tooth-Jointing Machine / Finger Joint Machine
- Cross-Laying / Lay-Up Table / Laminating Line
- Glue Mixing / Glue Blending Machine (Resin Blending Tank with Pump
- Double-Side Glue Spreader / Roller Spreader / Spray Applicator
- Cold Press / Pre-Press Hydraulic Press / Pneumatic Pre-Press
- Multi-Daylight / Multi-Plate Hot Press (Hydraulic Hot Press)
- Panel Trimming / Sizing Saw / CNC Router
- Edge Hot-Melt / Edge Banding Machines
- Wide-Belt Sander / Platen Sander / Calibrating Sander
- Polishing / UV Curing / Lacquer Line
- Moisture Meters / Bond Testing Equipment / Mechanical Test Rigs (Bending, Shear)
- Laser Measurement / Thickness Gauges / Surface Defect Scanners
- Chipper / Grinder / Briquette Press
- Effluent Treatment / Condensate Recovery
- Dust Collection (Cyclones / Bag Filters)
- Steam Boiler
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in a bamboo plywood manufacturing plant ranges between 60-70%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 15-30% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 15-20%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-15% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the bamboo plywood manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 10,000 cubic meter of bamboo plywood annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In June 2024, Prof. Naresworo Nugroho, IPB University's Bamboo Expert, has evolved bamboo into a substitute material that has enormous potential to become an excellent building material in keeping with technological advancements. Prof. Naresworo has created numerous technological advancements in engineered bamboo products through his research. These developments may serve as a robust and eco-friendly substitute for contemporary building materials.
Why Choose IMARC:
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104