Soap Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Production Cost Structure & Benchmarking

What is Soap?
Soap is a type of cleaning agent made by the chemical reaction of fats or oils and an alkali in a process known as saponification. The chemical reaction transforms triglycerides into soap, also known as fatty acid salts, giving these substances the properties of a surfactant, allowing the substance to be used for the removal of dirt, oil, and bacteria from surfaces. The soap molecule has the ability to encapsulate oil and other contaminants so that the contaminants can be easily removed by washing the substance away using water. Additionally, soap comes in solid, liquid, and semi-solid preparations that may have additional ingredients, for instance, fragrances, moisturizers, dyes, and antibacterial substances.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Soap is more commonly used in personal care, household, institutional, and industrial applications. For use in personal care, soap serves as an important product for hand wash, bathing, and skin cleaning. The soap plays an important role in ensuring that an individual achieves cleanliness by removing dirt, sweat, extra oils, and microbes. For personal care, soaps are typically made up of moisturizing ingredients, herbs, and non-stripping surfactants.
In the domestic setting, soap is applied as a cleaning agent for utensils, textiles, and surfaces. Laundry soaps and soaps in bar form are applied to eliminate stains and smell from clothes, while specialty soaps are applied to clean dishes and other household items. All of these functions are dependent on the ability of soap to degrade grease and organic materials.
Institutions like hospitals, schools, hotels, food processing plants, and offices require large amounts of soap as part of their hygienic purposes. Soap aids in infection control, food protection, as well as adherence to hygienic levels within these institutions. Other industrial applications include soap formulation for textile manufacture, metal cleaning, as well as machinery maintenance, which require emulsification as well as degreasing functionality.
Further, soap has niche market applications in cosmaceuticals, handmade craft products, and specialty cleaners for pets and sensitive surfaces. The versatility of soap in various dimensions of human life, from everyday activities to industrial practices, emphasizes its significance as a primitive cleaning aid.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global bath soap market reached a value of USD 24.6 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 35.0 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 3.57% during 2025-2033.
The main driver for the global soap market is attributed by the rising awareness of hygiene, health, and sanitation. The growing need for hand hygiene and personal cleanliness of the population is responsible for the continued demand for soap products in both developed and developing countries across the globe.
Population dynamics, or population growth, and urbanization play major roles. The growing population means that there will be more people demanding packaged consumer products such as personal care products, soaps, or other household detergents. The more organized people become, the less time they have, so they need a reliable way to keep themselves clean, promoting soap consumption.
The trend of work patterns and lifestyles is also another factor that impacts the Soap market. With the help of technological advancements, people are reliant on their Soaps for work from anywhere around the globe, online education, and on-demand services like online payment solutions, food delivery, and much more. Thus, with these trends, the market for Soap manufacturing is witnessing steady growth.
An increase in the demand for specialized and value-added products in the consumer segment also fuels the market. Rising demands for natural ingredients in soaps, skin compatibility, and beautification are witnessed as a result of increased consumer awareness with respect to the composition of the product and skin health.
Demand in the hospitality, healthcare, food service, and institutional industries add to the positivity. Here, huge volumes of soaps are required in these industries in order to meet the hygiene and operational requirements. This, in turn, allows for easy distribution of products and makes it easier for companies to reach new customers.
Environmental and sustainability factors also affect market dynamics. Demand for biodegradable and plant-based soaps drives companies to look for alternative ingredients and packaging. When added to demands for essential daily use, growth of the sector, and innovation, environmental factors have contributed to a steady growth of the global soaping industry.
Case Study on Cost Model of Soap Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale soap manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed soap manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 10,000 tons of soap annually.
Manufacturing Process: The making of soap entails a number of controlled chemical and physical processes that ensure the production of standardized soap products. The soap-making process starts with the selection of raw materials, which include fats or oils of vegetable or animal origins, along with an alkali, sodium hydroxide for soap making or potassium hydroxide for making liquid soap. The raw materials are accurately measured with the aim of achieving the right chemical equation for making soap.
The process of saponification sees the heating of oils and/or fats and the addition of the alkali solution in reactors or kettles. With controlled temperature and stirring, the process sees the reaction of triglycerides to produce soap and glycerin as a result of the reaction. The process can either follow the batch kettle process or the continuous process depending on how the soap is being manufactured. After the completion of the process of saponification, the soap mixture is left to settle, and excess water is removed.
The next step is purification and finishing. In some processes, salt is added to separate soap from glycerin, after which the soap is washed and refined. Additives like fragrance, colorants, moisturizers, preservatives, and functional agents are added in order to get the desired product characteristics. The soap mass is then homogenized to ensure uniform distribution of all ingredients.
In the case of bar soap, the finished soap is dried to the required moisture level, extruded into continuous logs, cut into bars, and stamped into final shapes. Liquid soap is diluted, filtered, and filled directly into containers. Quality control checks are performed along the process to check pH, texture, and appearance, along with other performance factors. The finished products are then packaged and prepared for distribution in accordance with consistency, hygiene, and safety standards.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
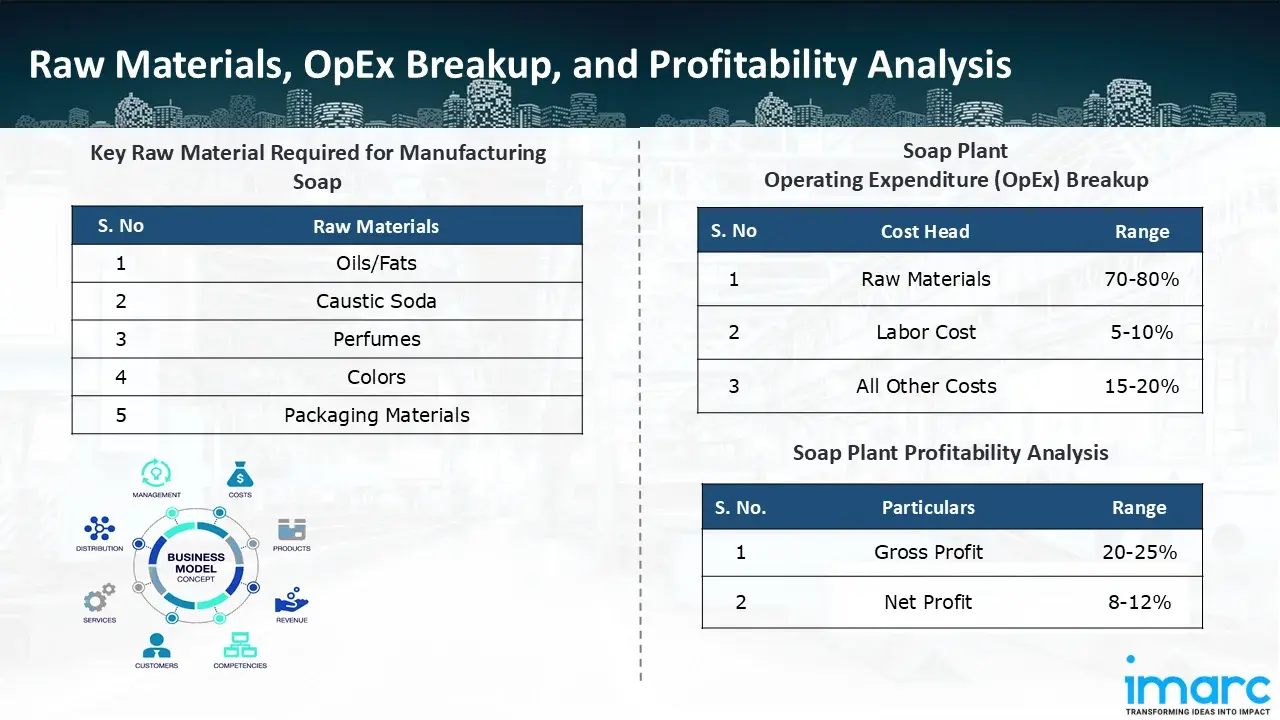
The basic raw materials required for soap manufacturing include:
- Oils/Fats
- Caustic Soda
- Perfumes
- Colors
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Saponification
- Drying
- Mixing
- Plodding
- Cutting
- Stamping
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in soap manufacturing plant ranges between 70-80%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 20-25%, and net profit lie between the range of 8-12% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the soap manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 10,000 tons of soap annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In January 2026, Santoor, the flagship soap brand of Wipro Consumer Care and Lighting (WCCL), has surpassed Hindustan Unilever's (HUL) Lifebuoy to exceed`2,850 crore in 2025 revenues, making it the most popular soap in India.
- In April 2025, AWL Agri Business has launched its latest product in personal care - Alife Gondhoraj & Neem Soap. This unique variant, which was introduced in West Bengal, combines the revitalising freshness of Gondhoraj lime with the tried-and-true cleansing properties of neem.
- In April 2025, Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Limited (KSDL), the company that produces the well-known Mysore Sandal Soap, announced preparing to introduce an ultra-luxury 150-gram "Mysore Sandal Millennium Super Premium Soap," which would cost Rs 3,000, with the goal of reaching the global market.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










