How Government Policies Are Driving the Japan Animal Feed Market

Introduction to Japan's Animal Feed Industry:
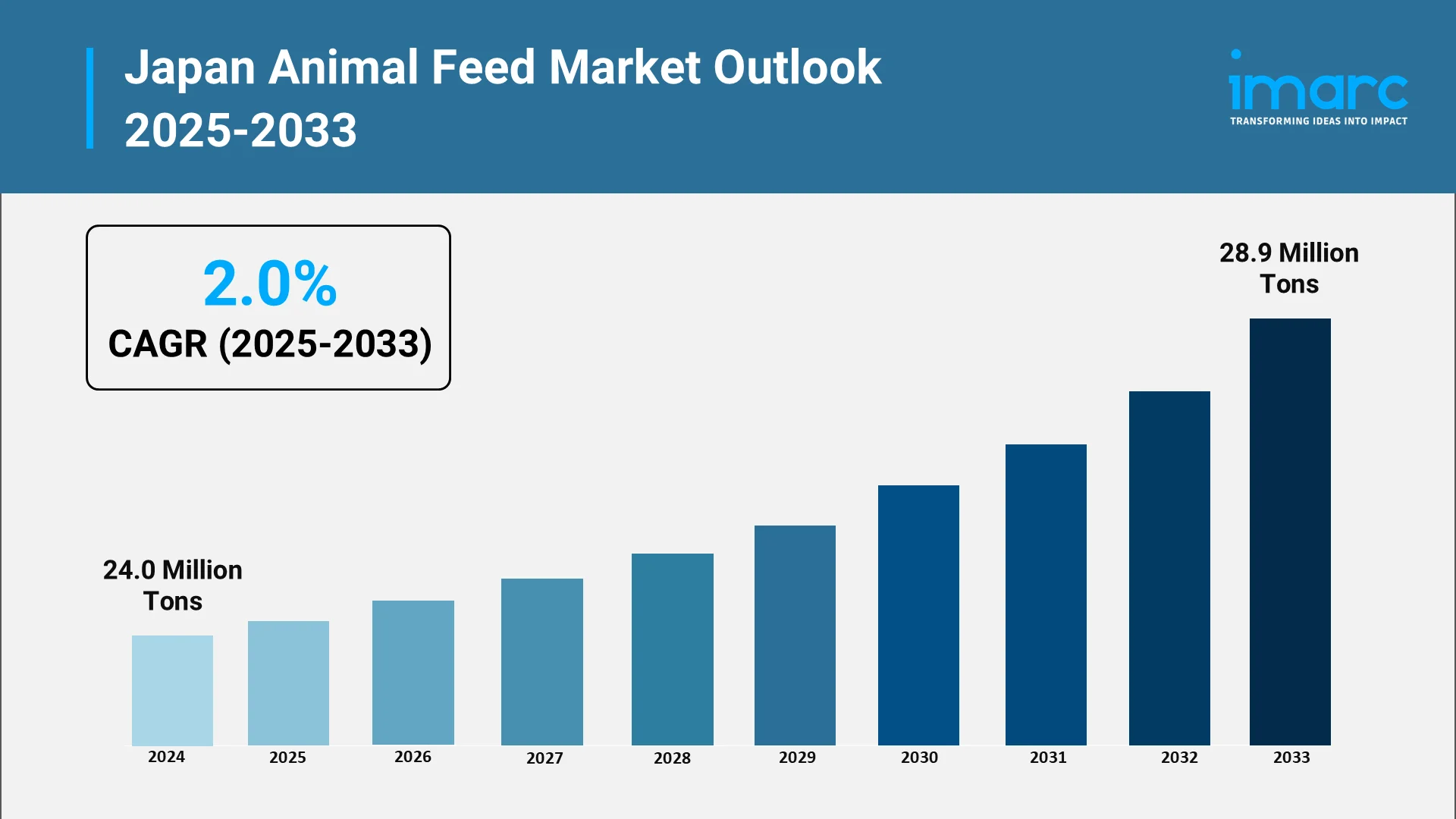
Japan's animal feed industry stands as a cornerstone of the nation's agricultural infrastructure, supporting domestic livestock production and ensuring food security. The sector encompasses diverse feed products for cattle, swine, poultry, and aquaculture operations that sustain Japan's protein supply chain. In 2024, the Japan animal feed market size reached 24.0 Million Tons.
Government intervention has emerged as the primary catalyst shaping Japan's animal feed market. Japanese policymakers have adopted a proactive stance in regulating, subsidizing, and steering the sector toward strategic national objectives. This comprehensive governmental approach addresses food security imperatives, environmental sustainability goals, animal welfare standards, and economic competitiveness.
The Japanese animal feed industry operates within a unique context characterized by limited arable land, high import dependency, and stringent quality expectations. These structural constraints have necessitated sophisticated policy interventions that balance competing priorities while maintaining the viability of domestic livestock operations.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
Overview of Government Regulations and Policy Framework:
Japan's regulatory architecture governing animal feed represents one of the most comprehensive systems globally. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) serves as the principal authority overseeing feed production, distribution, and utilization.
The regulatory framework defines permissible ingredients, manufacturing processes, labeling requirements, and quality specifications. Feed manufacturers must navigate a complex approval system before introducing products to market, ensuring compliance with established safety protocols.
Quality assurance mechanisms form the backbone of Japan's feed regulation system. Mandatory testing protocols verify the absence of prohibited substances and detect potential contaminants that could compromise animal health or food safety.
The government has established clear traceability requirements enabling authorities to track feed ingredients from source to consumption. This transparency facilitates rapid response capabilities should safety concerns arise while providing consumers with confidence in domestically produced animal proteins.
Japan's regulatory framework addresses emerging challenges related to antimicrobial resistance, establishing restrictions on medicated feed usage. The regulatory environment shapes competitive dynamics, with compliance costs creating barriers to entry for smaller players while established manufacturers gain competitive advantages.
Subsidies and Support Programs for Livestock Farmers:
Financial assistance programs administered by the Japanese government constitute a fundamental pillar supporting the nation's livestock sector. These initiatives reflect strategic recognition that maintaining viable domestic livestock operations requires sustained policy support.
Direct subsidies for feed procurement represent the most visible form of government support, reducing the financial burden on livestock farmers. These programs acknowledge that Japanese farmers face significantly higher input costs compared to international competitors. By offsetting feed expenses, the government enables livestock operations to remain economically viable.
Support programs extend beyond price subsidies to encompass comprehensive assistance for farm modernization. Government funding facilitates investments in advanced feeding systems, precision livestock management technologies, and infrastructure upgrades that enhance productivity while reducing waste.
The government has established specialized programs targeting specific livestock sectors. Dairy operations, beef producers, swine farmers, and poultry enterprises each access tailored support reflecting their unique economic circumstances and strategic importance to food security objectives.
Risk management programs provide safety nets against volatile feed prices. Given Japan's dependence on imported feed ingredients, international commodity price fluctuations can dramatically impact farmer profitability. Government stabilization mechanisms cushion producers from extreme price movements.
Support programs increasingly incorporate sustainability criteria, incentivizing environmentally responsible feeding practices. According to Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF), as Japan pursues its ambitious goal of raising feed self-sufficiency from 38% percent to 45% by 2030. These subsidies encourage farmers to transition paddy fields to feed crop production, addressing oversupply in food-grade rice market while reducing import dependence. Technical assistance programs connect producers with expertise in nutrition management and emerging technologies, building farmer capacity to compete effectively.
Sustainability and Feed Safety Standards in Japan:
Environmental sustainability has emerged as a defining priority within Japan's animal feed policy framework. The government has established ambitious benchmarks for reducing the environmental footprint of livestock production, with feed-related initiatives playing central roles.
Feed efficiency standards encourage optimization of nutrient utilization, reducing the quantity of feed required per unit of livestock output. Regulatory guidelines promote adoption of precision feeding approaches that match nutrient supply with animal requirements accurately.
The promotion of alternative feed ingredients represents a strategic thrust within Japan's sustainability agenda. Government policies incentivize utilization of food manufacturing byproducts, insect proteins, and unconventional ingredients that reduce reliance on conventional feed grains, decreasing import dependency and minimizing food waste.
Carbon footprint reduction goals influence feed policy across multiple dimensions. The government supports development of locally sourced feed ingredients that minimize transportation emissions and encourages adoption of feed formulations that reduce enteric methane emissions from ruminant livestock.
Feed safety standards in Japan rank among the world's most stringent. Comprehensive testing requirements screen for mycotoxins, heavy metals, pesticide residues, and microbiological hazards. The government maintains zero-tolerance policies for specified prohibited substances. Recent advances in mycotoxin detection have improved safety monitoring, with new research published in 2024-2025 focusing on rapid screening methods for aflatoxin B1 using enhanced ELISA techniques and LC-MS/MS technology. In September 2024, Japan's Consumer Affairs Agency revised specifications and standards for food contact materials, establishing standardized overall migration tests to measure substances that could migrate from packaging materials into food, with the revised methods becoming effective in June 2026.
Traceability requirements enable rapid identification of contaminated feed batches should safety incidents occur. Mandatory documentation systems create accountability throughout the supply chain, building consumer confidence while providing authorities with tools to protect public health.
Impact of Trade Policies and Import Regulations:
Trade policies exert profound influence over Japan's animal feed market given the nation's substantial dependence on imported ingredients. The government employs a sophisticated array of tariffs, quotas, sanitary requirements, and bilateral agreements that shape import patterns.
Import regulations establish rigorous prerequisites for foreign suppliers. Exporting countries must demonstrate compliance with Japanese safety standards, often requiring certification from recognized authorities. These measures ensure imported ingredients meet stringent standards applied to domestic production.
Tariff structures influence the relative economics of different feed ingredients. The government adjusts tariff levels strategically to balance ensuring affordable feed availability for livestock farmers while providing some protection for domestic producers.
Japan participates in numerous trade agreements that shape feed ingredient import conditions. These agreements establish preferential access arrangements for partner nations and create frameworks for addressing trade disputes.
Strategic stockpiling programs complement trade policies, with the government maintaining reserves of critical feed ingredients to buffer against supply disruptions. These stockpiles provide insurance against international market volatility and geopolitical events that could threaten supply continuity.
The government actively promotes diversification of import sources, reducing vulnerability to supply disruptions. Import regulations increasingly incorporate sustainability criteria, with preferences extended to suppliers demonstrating environmental stewardship.
Japan's participation in international forums provides platforms for advocating national interests while contributing to global governance frameworks. Trade policy coordination with major feed ingredient exporters proves essential for maintaining stable supply relationships.
Future Outlook: Policy-Driven Growth in Japan's Animal Feed Market
According to the IMARC Group, the market is expected to reach 28.9 Million Tons by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 2.0% during 2025-2033. The Japanese animal feed market's future trajectory will be determined largely by evolving government policies responding to emerging challenges and opportunities.
Climate change adaptation represents a critical policy frontier that will increasingly shape feed market dynamics. The government recognizes that climate-related disruptions could threaten feed ingredient supply chains. Anticipated policy responses include intensified support for local feed production capacity, accelerated development of climate-adapted feed crops, and incentives for incorporating drought-resistant ingredients.
Technological innovation will receive expanded policy support. Government programs will likely increase funding for research into precision feeding systems, artificial intelligence applications in feed formulation, and biotechnology approaches to developing novel protein sources.
Circular economy principles will permeate feed policies more extensively, with enhanced incentives for converting food industry byproducts into valuable feed ingredients. The government will likely establish more comprehensive frameworks supporting food waste valorization and insect farming for feed protein.
International cooperation on feed standards and trade facilitation will intensify as Japan seeks to maintain secure access to global ingredient markets. Animal welfare considerations will assume greater prominence in policy formulation, reflecting evolving societal values.
Policy support for alternative proteins will expand, accelerating commercialization of insect-based feeds, single-cell proteins, and other innovative ingredients. The government recognizes that diversifying protein sources enhances supply security while addressing environmental concerns.
Digital transformation of the feed industry will receive policy encouragement, with potential support for blockchain-based traceability systems and digital marketplaces connecting feed suppliers with livestock farmers.
Collaboration between government and private sector will deepen through public-private partnerships targeting shared objectives. These collaborative arrangements will mobilize private sector innovation while leveraging government resources and regulatory authority.
The Japanese government's continued commitment to proactive feed market governance positions the sector for sustained development aligned with national priorities. Stakeholders who understand this policy-driven environment will be best positioned to capitalize on opportunities within Japan's dynamic animal feed market.
Partner with IMARC Group for Strategic Intelligence in Animal Feed Markets:
Choose IMARC Group as your trusted advisor for navigating the complex dynamics of global animal feed markets. We deliver unmatched expertise and comprehensive services tailored to your strategic objectives:
- Data-Driven Market Research: Gain deep insights into feed ingredient trends, livestock production patterns, regulatory developments, and technological innovations transforming the animal nutrition sector through our authoritative market intelligence reports.
- Strategic Growth Forecasting: Anticipate emerging opportunities in alternative proteins, precision feeding technologies, sustainability-focused formulations, and regional market expansions with our forward-looking analysis of industry trajectories.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Understand competitive positioning within feed manufacturing, ingredient supply, and livestock production sectors through detailed analysis of market participants, strategic initiatives, and innovation pipelines.
- Policy and Regulatory Advisory: Navigate evolving regulatory frameworks, trade policies, and sustainability requirements affecting feed markets globally with expert guidance on compliance strategies and advocacy opportunities.
- Custom Reports and Consulting: Access bespoke intelligence aligned with your specific needs—whether entering new geographic markets, evaluating investment opportunities, assessing technological innovations, or optimizing feed supply chains.
At IMARC Group, we empower animal agriculture stakeholders with the clarity and intelligence required to make confident strategic decisions in an increasingly complex global marketplace. Partner with us to transform market insights into competitive advantages—because informed decisions drive sustainable success. For more details, click on this link: https://www.imarcgroup.com/japan-animal-feed-market
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










