Saffron Processing Cost Analysis: Harvesting Luxury

What is Saffron?
Saffron is one of the world’s most precious natural spices, derived from the dried red stigmas of the Crocus sativus flower. Each bloom yields only a few delicate stigmas, which must be carefully hand-harvested, dried, and processed to preserve their vibrant color, distinctive aroma, and rich flavor. The spice’s deep golden-yellow hue, bitter-sweet taste, and unique fragrance are primarily attributed to its key bioactive compounds like crocin, picrocrocin, and safranal. Because of the crop’s short flowering season, delicate handling requirements, and labor-intensive harvesting process, saffron commands one of the highest prices among spices globally. It is traded in thread, powdered, and extract forms, serving as a luxury ingredient across multiple industries.
Key Applications Across Industries:
Saffron’s versatility spans culinary, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, cosmetic, and fragrance industries, where it is prized for its sensory and functional attributes.
In the food and beverage industry, saffron is used as a natural flavoring and coloring agent in both traditional and modern cuisines. It enriches rice dishes, desserts, baked goods, confectionery, dairy products, beverages, and sauces, imparting its signature aroma, taste, and golden hue. Food manufacturers and gourmet brands also use saffron to enhance product differentiation, authenticity, and perceived luxury in premium offerings.
In pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, saffron is valued for its bioactive compounds known for their antioxidant, mood-supporting, and cognitive-enhancing properties. Standardized saffron extracts are incorporated into dietary supplements, capsules, and functional foods designed to promote mental well-being, eye health, and general vitality. Historically, in traditional medicine systems, saffron has been used to support digestive, respiratory, and circulatory functions, reflecting its wide therapeutic heritage. The cosmetic and personal care sector also utilizes saffron for its skin-brightening, antioxidant, and anti-aging properties. It is commonly found in premium creams, serums, facial masks, and soaps, particularly within herbal and luxury skincare lines. In perfumery, saffron contributes warm, spicy, and leathery notes to high-end fragrances, adding depth and sophistication to their aromatic profiles.
Beyond commercial applications, saffron holds cultural significance and is used in religious, ceremonial, and traditional practices across many regions. Its enduring appeal across food, wellness, beauty, and cultural segments underscores its reputation as a symbol of luxury, purity, and tradition.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global saffron market reached a value of USD 600.3 Million in 2025. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 1,110.7 Million by 2034, at a projected CAGR of 7.08% during 2026-2034. The global saffron market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for natural, premium, and multifunctional ingredients across diverse sectors including food, wellness, and cosmetics.
One of the primary market drivers is the rising consumer shift toward natural and clean-label products. As synthetic colors and flavoring agents face regulatory and consumer scrutiny, saffron’s dual role as a natural flavorant and functional ingredient makes it a preferred choice for health-conscious and premium brands. The nutraceutical and wellness sectors represent a significant growth area. Scientific research validating saffron’s benefits for mood regulation, stress reduction, and cognitive support has spurred its use in dietary supplements and health formulations. This shift has expanded saffron’s value chain from raw spice production to standardized extracts and bioactive ingredient manufacturing.
Culinary globalization also plays a key role. The growing popularity of international cuisines and gourmet dining has expanded saffron’s use in foodservice and packaged food products, where it enhances authenticity and visual appeal. Similarly, rising disposable incomes and luxury consumption trends in emerging economies have increased demand for saffron in premium foods, gift products, and high-end cosmetics. Furthermore, improvements in processing technologies, drying techniques, and grading systems have enhanced product quality, yield consistency, and export potential. The rise of traceability programs, origin-based certifications (such as PDO/PGI), and quality assurance standards has strengthened consumer trust and premium positioning in global markets.
Although saffron cultivation remains geographically limited and labor-intensive, the market’s value-added processing, extract development, and branding innovations continue to drive commercial viability. In summary, the global saffron market is being shaped by natural ingredient trends, wellness-driven demand, culinary innovation, and sustainability-focused production factors that together ensure continued growth and enduring prestige for this golden spice.
Case Study on Cost Model of Saffron Processing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale saffron processing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed saffron processing plant in India. This plant is designed to process 1,000 kg of saffron annually.
Processing Flow: The manufacturing process of saffron is a meticulous, labor-intensive, and quality-sensitive operation designed to preserve the spice’s signature aroma, vivid color, and bioactive compounds. Every step, from harvesting to packaging, requires precision and care to maintain saffron’s premium quality and value. Processing begins immediately after harvesting the Crocus sativus flowers, which are hand-picked during the early morning hours to prevent wilting and damage. The first and most delicate operation is stigma separation, where the three red stigmas are carefully detached from each flower by hand. This process is carried out under hygienic and controlled conditions to avoid contamination and ensure uniform quality across batches.
Once separated, the drying stage begins, widely regarded as the most critical step in saffron processing. Drying reduces the moisture content of the stigmas while preserving and stabilizing the spice’s key bioactive components: crocin (color), picrocrocin (flavor), and safranal (aroma). Traditional drying techniques involve shade drying, air drying, or gentle heat drying, whereas modern facilities use temperature- and humidity-controlled dryers to achieve consistent, high-quality results. The process must be carefully managed: overheating can destroy color and aroma, while inadequate drying can cause mold growth or spoilage.
After drying, the saffron threads are cooled, conditioned, and stabilized to maintain their chemical balance and sensory properties. The dried threads are then graded based on several quality parameters, including color intensity, aroma strength, thread length, and purity. Advanced processors may employ spectrophotometric or chromatographic analyses to measure active compound levels and detect adulteration, ensuring authenticity and compliance with international quality standards.
Depending on the market requirement, the graded saffron may be retained as whole threads (for premium culinary use) or milled into powder under controlled conditions to prevent oxidation and preserve volatile aromatic compounds.
The final step involves packaging, which plays a crucial role in maintaining saffron’s integrity. The product is packed in airtight, moisture-proof, and light-resistant containers to protect it from environmental degradation during storage and transportation. In value-added processing, saffron may undergo extraction and standardization to produce concentrated forms such as saffron oleoresins or extracts, which are widely used in nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic formulations.
Throughout the entire process, strict quality control, hygiene, and traceability protocols are maintained to guarantee authenticity, safety, and consistent premium quality. This meticulous approach, from flower to finished product, ensures that saffron retains its status as one of the most valuable and sought-after natural spices in the world.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for saffron processing include:
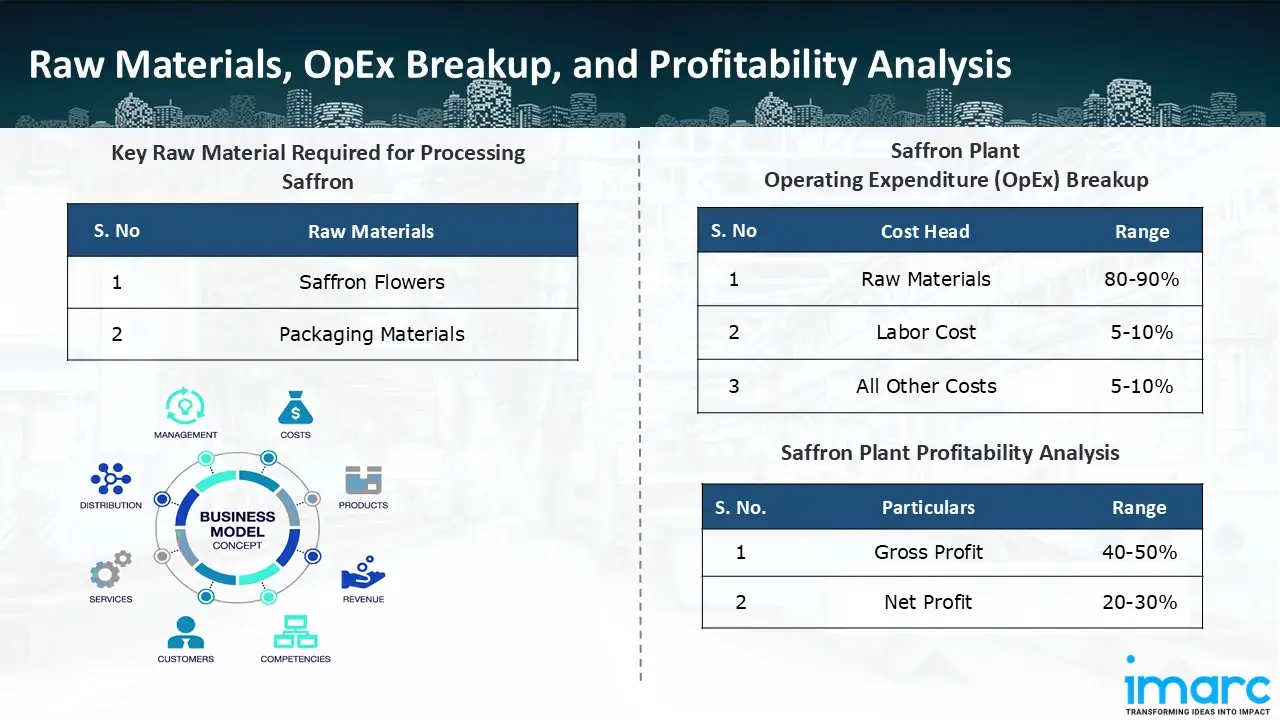
- Saffron Flowers
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Harvesting
- Separation
- Drying
- Grading
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a processing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a processing plant effectively. OpEx in a processing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a processing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in saffron processing plant ranges between 80-90%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 5-10% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 40-50%, and net profit lie between the range of 20-30% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the saffron processing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, processing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of processing 1,000 kg of saffron annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale processing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In February 2025, Jebel Ali Free Zone (Jafza) has teamed with the well-known Indian global food company Haldiram's to establish one of the biggest saffron processing plants in the Gulf Cooperation Council, following an agreement struck on the margins of Gulfood in Dubai.
- In May 2024, Saffron Tech introduces its innovative pilot plant, transforming saffron farming with economical techniques for industrial production. The facility advances the company's goal of making saffron more accessible globally by streamlining cultivation procedures and improving sustainability through the integration of cutting-edge technology and creative agronomy.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the processing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish processing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










