PVC Pipes Manufacturing Cost Analysis: The Pipeline Equation

What are PVC Pipes?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are durable and versatile piping products made from a synthetic thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, chemical resistance, and longevity. These pipes are produced primarily through the extrusion process, which ensures consistent wall thickness and uniform mechanical properties. Available in both rigid and flexible forms, PVC pipes are designed to transport fluids, gases, or solids safely under controlled pressure and temperature conditions. Lightweight yet strong, PVC pipes resist corrosion, scaling, and most chemical reactions, making them suitable for long-term applications in various environments. They are available in a wide range of diameters, wall thicknesses, and pressure ratings, allowing them to meet specific requirements in industries such as water supply, construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. From potable water distribution to industrial fluid handling, PVC pipes have become an essential component of modern infrastructure and utilities.
Key Applications Across Industries:
PVC pipes are extensively used across infrastructure, agriculture, construction, and industrial sectors due to their durability, cost efficiency, and ease of installation. In water supply systems, PVC pipes are a preferred choice for potable water distribution in residential, commercial, and municipal networks. Their corrosion resistance and smooth interior surface ensure minimal frictional losses, supporting efficient water flow and extended service life. For sanitation and drainage, PVC pipes are widely employed in sewage systems, stormwater drainage networks, and waste discharge lines. Their high resistance to chemicals and biological degradation allows them to perform reliably in both underground and exposed installations.
In agriculture, PVC piping systems play a vital role in irrigation including drip and sprinkler systems helping farmers achieve efficient water management and higher crop productivity. Their light weight and simple jointing systems make them easy to install and maintain in the field. Within the construction industry, PVC pipes are used for plumbing, rainwater harvesting, ventilation, and as conduits for electrical wiring. Their non-conductive, fire-retardant, and waterproof nature ensures safety and long-term reliability in residential and commercial structures.
Industrial applications are equally diverse. PVC pipes are used to transport process water, acids, alkalis, and other chemicals in factories, power plants, and treatment facilities. They are also utilized in swimming pools, aquaculture systems, and HVAC installations, where durability and chemical stability are essential. Thanks to their lightweight design, compatibility with a wide range of fittings, and low maintenance requirements, PVC pipes have become indispensable across both everyday utility networks and specialized engineering applications.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global PVC pipes market reached a volume of 25.90 Million Tons in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach 36.30 Million Tons by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 3.8% during 2025-2033. The global PVC pipes market continues to expand, driven by infrastructure growth, urbanization, and increasing demand for efficient water management systems. Rapid population growth and urban expansion, particularly in emerging economies, are fueling large-scale construction of housing, commercial buildings, and public utilities — all of which depend on reliable and cost-effective piping systems. PVC pipes are favored for such projects due to their affordability, long service life, and ease of handling.
Government-led initiatives in water supply, sanitation, and irrigation are major contributors to market growth. Programs aimed at improving access to clean drinking water, expanding sewage and drainage networks, and modernizing agricultural irrigation systems rely heavily on PVC piping solutions. The combination of durability and low maintenance costs makes these systems ideal for long-term infrastructure investments.
The agriculture sector also plays a significant role. As farmers adopt modern irrigation methods to optimize water usage and enhance crop yields, PVC pipes provide an efficient, low-cost means of water delivery. With growing concerns about water scarcity and sustainability, the demand for durable, leak-resistant piping materials continues to rise.
In industrial sectors, expansion in manufacturing, chemical processing, and energy production has further boosted the use of PVC pipes. Their ability to handle a wide range of fluids without corrosion or chemical degradation makes them a practical alternative to metal piping in non-high-temperature applications.
Material and technological advancements continue to shape the market as well. Modern PVC formulations offer improved strength, flexibility, and fire-retardant properties, while enhanced extrusion technologies allow for higher precision and product consistency. The pipes’ light weight also reduces transportation and installation costs, contributing to overall project efficiency.
Lastly, sustainability trends and stricter environmental regulations are encouraging the adoption of recyclable, energy-efficient materials. PVC pipes meet these criteria, offering a long lifespan with minimal environmental impact compared to traditional materials. Together, these factors including rising infrastructure investment, agricultural modernization, industrial expansion, and sustainability awareness are driving sustained global growth in the PVC pipe manufacturing industry.
Case Study on Cost Model of PVC Pipes Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale PVC pipes manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed PVC pipes manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 10,000 tons of PVC pipes annually.
Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing of PVC pipes follows a carefully controlled series of steps including material preparation, extrusion, cooling, and finishing, each designed to produce pipes with consistent dimensions, strength, and performance characteristics.
The process begins with compound formulation, where polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin is blended with stabilizers, lubricants, impact modifiers, fillers, and pigments. Each additive serves a specific function: stabilizers enhance heat and UV resistance, lubricants improve processability, impact modifiers increase toughness, and pigments provide color and appearance. The composition of the compound is precisely controlled to achieve the desired balance of rigidity, pressure resistance, and long-term durability. Thorough mixing ensures even dispersion of additives, resulting in a uniform and high-quality PVC compound.
The prepared material is then fed into an extrusion line, where it is heated and melted inside a single- or twin-screw extruder. Within the extruder, the molten PVC is homogenized and pressurized before being forced through a specially designed pipe die, which shapes it into a continuous cylindrical form. As the hot pipe exits the die, it immediately enters a vacuum calibration tank, where vacuum pressure and cooling water work together to control its external diameter and wall thickness with high precision.
After calibration, the pipe passes through additional cooling tanks to fully solidify the material and stabilize its dimensions. It is then drawn forward by haul-off units that maintain a steady pulling speed and consistent tension, ensuring smooth surfaces and uniform thickness.
In the finishing stage, the pipe is cut to standard lengths using automatic cutting machines. Depending on the product type, additional operations such as socketing or belling may be performed, where one end of the pipe is expanded to facilitate easy jointing and installation.
Throughout production, quality-control checks are carried out at multiple stages to verify dimensional accuracy, surface finish, pressure resistance, and impact strength. Only pipes that meet strict performance standards proceed to marking, bundling, and packaging for storage and distribution.
Modern PVC pipe manufacturing plants emphasize automation, precision control, and sustainability. Advanced systems monitor temperature, pressure, and extrusion speed to ensure consistent output, while material recycling and energy-efficient technologies help reduce environmental impact. The result is a high-quality, durable, and sustainable piping product suited for a wide range of infrastructure and industrial applications.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
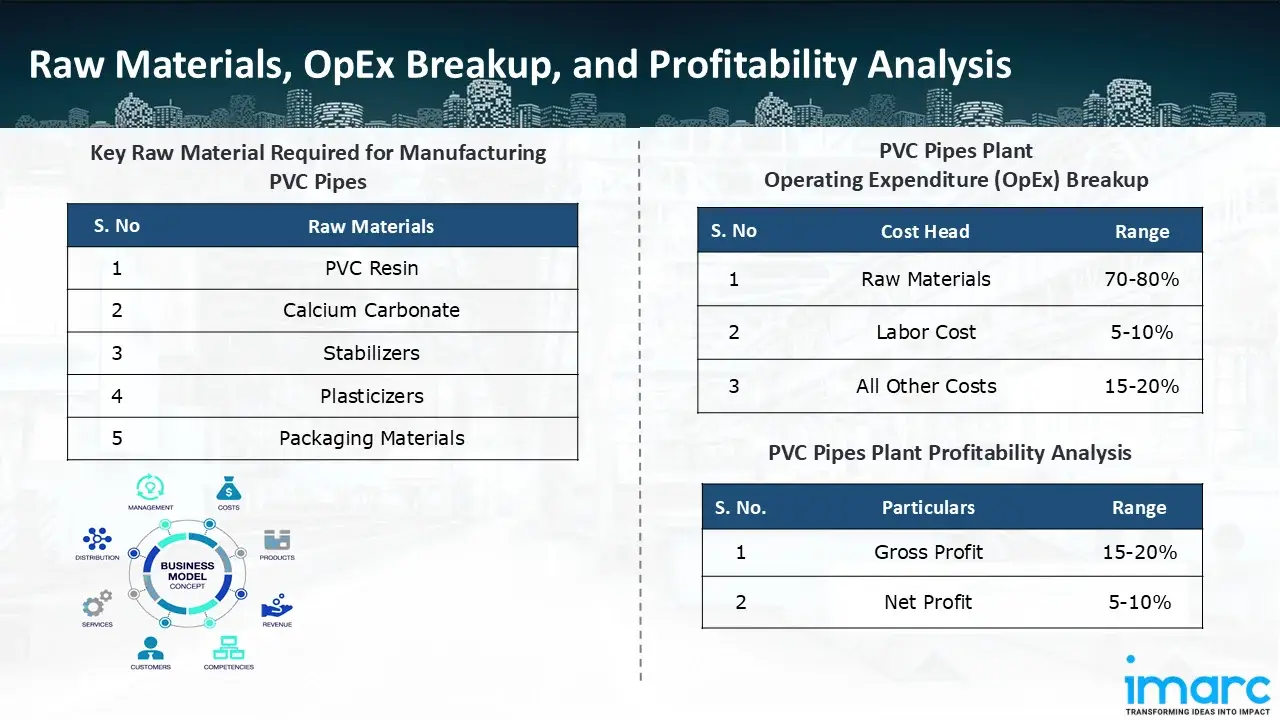
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for PVC pipes manufacturing include:
- PVC Resin
- Calcium Carbonate
- Stabilizers
- Plasticizers
- Packaging Materials
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- Mixing
- Extrusion
- Cooling
- Printing
- Cutting
- Packing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. OpEx in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in PVC pipes manufacturing plant ranges between 70-80%, labor cost ranges between 5% to 10%, and all other costs ranges between 15-20% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 15-20%, and net profit lie between the range of 5-10% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the PVC pipes manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 10,000 tons of PVC pipes annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2025, the Urban Infrastructure & Environmental Products Company has been working on a novel technology for PFAS-free pipe materials for ultrapure process applications in the production of sophisticated semiconductors, according to SEKISUI CHEMICAL CO., LTD.
- In March 2025, the DS Jindal Group, a pioneer in the production of premium pipes, is pleased to announce the opening of its newest Jindal PVC Manufacturing Unit in Pantnagar, Uttarakhand.
- In August 2024, Aliaxis SA, a global leader enabling access to water and energy through innovative fluid management solutions, announced that it has closed the deal to acquire the manufacturing assets of Johnson Controls’ CPVC pipe and fittings business for residential and light commercial sprinkler systems.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104










