GCC Cement Market Trends: Navigating Construction Demand and Industrial Growth

Introduction:
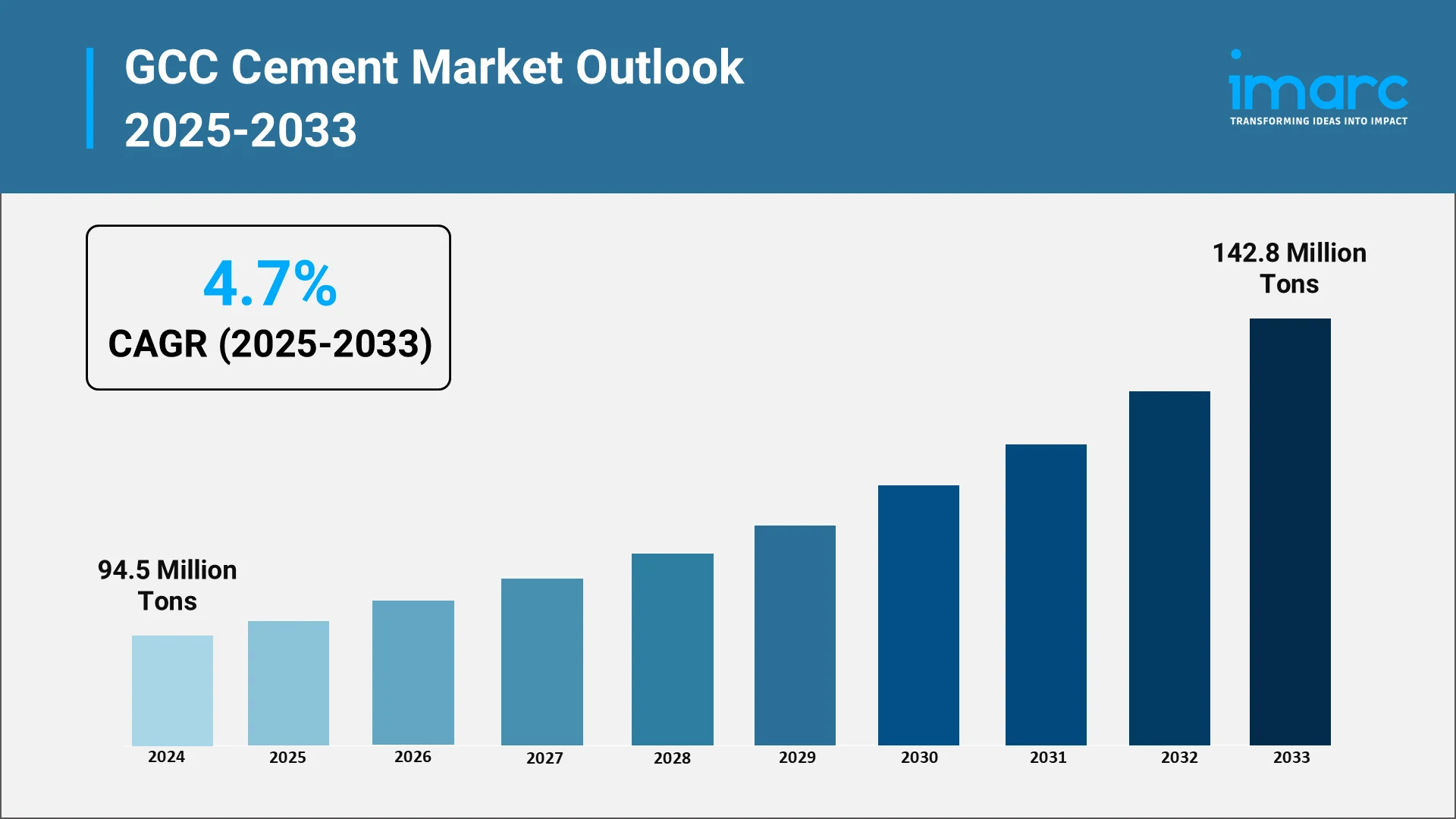
The Gulf Cooperation Council cement market stands at a critical juncture as regional economies accelerate infrastructure development and pursue ambitious economic diversification strategies. Cement consumption across the GCC nations continues to expand, driven by transformative megaprojects, rapid urbanization, and substantial government investment in construction infrastructure. The sector plays an essential role in supporting the region's transition toward post-oil economies, with demand patterns reflecting both immediate construction needs and long-term developmental objectives. The GCC cement market size reached 94.5 Million Tons in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach 142.8 Million Tons by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% during 2025-2033.
Regional cement demand is experiencing robust momentum, particularly in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, where large-scale construction initiatives have created sustained consumption growth. Cement sales in Saudi Arabia increased substantially in the fourth quarter of 2024, reaching approximately 14.87 million tonnes, primarily driven by strong domestic demand. This growth trajectory underscores the sector's fundamental importance to GCC economic transformation plans and highlights the dynamic nature of GCC cement industry growth.
The cement industry's expansion directly correlates with massive infrastructure investments and residential construction activity. The Saudi cement sector supports a booming construction market driven by massive infrastructure projects under the Vision 2030 initiative, including NEOM, the Red Sea Project, and FIFA World Cup-related construction. These developments create sustained, long-term cement demand that extends well beyond immediate project timelines, establishing a foundation for continued sectoral growth through the end of this decade.
Industrial expansion and commercial development further amplify cement consumption across the region. The GCC's strategic geographic position, coupled with government policies promoting economic diversification, has catalyzed investments in manufacturing facilities, logistics hubs, and commercial centers. Each of these initiatives requires substantial quantities of cement and concrete products, reinforcing the construction materials sector as a cornerstone of regional development strategies. The interplay between government-led megaprojects, private sector investments, and demographic growth patterns positions the GCC cement market for sustained expansion as nations work to realize their respective economic visions, with GCC cement market trends pointing toward increased emphasis on sustainability and technological innovation.
Explore in-depth findings for this market, Request Sample
How Vision 2030 is Transforming the GCC Cement Industry:
Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 initiative represents a watershed moment for the regional cement sector, fundamentally reshaping demand patterns and industry dynamics across the Gulf. Saudi Arabia's cement industry is well-positioned to meet growing demand spurred by developments like NEOM, the Red Sea Project, and FIFA World Cup-related construction, with the sector playing a critical role in the Kingdom's industrial landscape. This transformative agenda has catalyzed unprecedented construction activity, with megaprojects requiring vast quantities of cement to materialize ambitious development plans. The initiative's emphasis on tourism, entertainment, technology, and industrial diversification has created multiple demand streams, each contributing to sustained cement consumption. Beyond Saudi Arabia, other GCC nations have launched parallel initiatives that mirror Vision 2030's developmental ambitions. The UAE's economic diversification efforts, Qatar's post-World Cup infrastructure investments, and region-wide smart city developments collectively generate substantial cement requirements. Megaprojects under Vision 2030 such as NEOM, The Line, Red Sea Project, and Qiddiya are driving cement consumption in multiple regions, with companies realigning logistics and dispatch operations to serve these locations efficiently. This coordinated regional development approach has transformed the GCC cement market from a traditional construction materials sector into a strategic enabler of economic transformation, with producers adapting capacity, technology, and sustainability practices to meet the evolving demands of next-generation infrastructure projects.
Key Industry Trends:
Rising Demand from Mega Infrastructure Projects
The GCC cement industry is experiencing unprecedented demand driven by transformational infrastructure initiatives that define the region's developmental trajectory. Projects such as NEOM, a $500 billion futuristic city, and the Red Sea Project, focused on luxury tourism and real estate, are creating substantial demand for construction materials, with the Red Sea Project alone planning to develop over 50 resorts and 8,000 hotel rooms by 2030. These megaprojects represent more than isolated construction endeavors; they constitute comprehensive urban ecosystems requiring sustained cement supply over multi-year development horizons.
The scale of infrastructure investment across the Gulf necessitates massive material quantities. Industry experts anticipate maximum cement demand in Saudi Arabia could reach 78 million tonnes annually over the next five years to support megaprojects and infrastructure developments. This sustained consumption creates stable market conditions for cement producers while demanding operational excellence and logistical sophistication to meet project-specific requirements and timelines, directly impacting GCC cement market forecast projections.
Beyond headline megaprojects, systematic infrastructure modernization across transportation networks, utilities, and civic facilities generates consistent baseline demand. Municipal infrastructure and housing developments sustain base demand, with public housing schemes and roadworks generating consistent consumption, as companies secure multi-year supply contracts linked to road, sewage, and utility infrastructure upgrades. This combination of spectacular giga-projects and essential infrastructure work creates a balanced demand profile that supports industry stability and growth.
Expansion of Green Cement and Low-Carbon Production Technologies
Environmental sustainability has emerged as a defining priority for the GCC cement industry, with producers increasingly adopting low-carbon technologies and green cement formulations. The global cement industry has achieved a 25% reduction in carbon dioxide per tonne of cementitious material since 1990, with companies implementing carbon capture utilization and storage which accounts for 36% of the industry's planned emissions reductions. This decarbonization momentum reflects both regulatory pressure and corporate commitment to environmental stewardship.
Cement manufacturers across the Gulf are investing in alternative materials and production methods that reduce carbon footprints. Yamama Cement and Arabian Cement have introduced refuse-derived fuel into kilns at pilot scale, aligned with Saudi Green Initiative goals, with cement producers signing agreements with municipalities and waste firms to source biomass and industrial waste for thermal energy substitution. These innovations demonstrate practical pathways toward sustainable production without compromising output capacity or product quality.
The transition toward green cement aligns with broader regional sustainability objectives while responding to evolving market preferences. The projected expansion of green cement is driven by mega projects like Saudi Arabia's NEOM achieving green ambitions, with tighter green building regulations and increasing awareness accelerating adoption in the UAE and Saudi Arabia. As environmental consciousness permeates construction practices, green cement adoption will likely accelerate, establishing sustainability as a competitive differentiator rather than merely a regulatory compliance requirement, thereby influencing the overall GCC cement market size and composition.
Increasing Investment in Clinker Capacity and Production Optimization
Strategic capacity expansions and production optimization initiatives characterize the contemporary GCC cement landscape. Sinoma Overseas marked the construction of a preheater tower as part of a relocation and upgrade of Yamama Cement's production line, with the expansion increasing capacity from 10,000 tons per day to 12,500 tons per day. These investments reflect producer confidence in sustained demand growth while incorporating advanced technologies that enhance operational efficiency.
Clinker production capacity adjustments respond to evolving market dynamics and project-specific requirements. Saudi cement companies produced 14.89 million tonnes of clinker in the fourth quarter of 2024, representing a 7 percent increase from the corresponding period in 2023, with clinker inventories growing 14 percent annually. This inventory growth provides strategic flexibility, enabling producers to respond rapidly to demand surges associated with major project phases.
Production optimization extends beyond mere capacity additions to encompass technological modernization and digital transformation. Major producers are implementing predictive maintenance, digital fuel mix optimization, and automated emissions tracking as part of digital plant upgrades improving efficiency and compliance. These operational enhancements position GCC cement producers to compete effectively in increasingly sophisticated markets while managing cost structures and environmental performance.
Growth of Public-Private Partnerships in Construction and Urban Development
Public-private partnerships have become instrumental mechanisms for accelerating infrastructure development across the GCC, with implications for cement demand patterns and market structure. Governments increasingly leverage private sector expertise, capital, and efficiency to realize ambitious construction agendas, creating collaborative frameworks that distribute risk while expediting project delivery. These partnership models facilitate larger-scale developments than purely public initiatives might achieve, thereby amplifying overall cement consumption. For instance, in October 2025, The Nemetschek Group, a global leader in AEC/O software solutions, entered a partnership with WakeCap Technologies, a top construction tech firm in the region known for its sensor-based, real-time project management systems. This strategic alliance aims to fast-track digital transformation throughout the GCC’s construction sector.
The partnership approach extends to materials supply arrangements, where cement producers engage directly with project developers to ensure reliable, specification-compliant product delivery. Companies are entering logistics-sharing agreements and clinker swap arrangements to improve plant utilization across high-demand zones, with Eastern Province Cement partnering with local logistics firms to streamline dispatch to Red Sea coast developments. These collaborative arrangements optimize supply chain efficiency while reducing environmental impacts associated with long-distance transportation.
Infrastructure financing innovations associated with public-private partnerships create new opportunities for cement sector participants. As governments establish regulatory frameworks conducive to private investment in traditionally public sectors, cement producers can develop strategic relationships with infrastructure developers, potentially securing long-term supply agreements that provide revenue visibility and support capital investment decisions. This evolving partnership landscape represents a structural shift in how major construction projects are conceived, financed, and executed across the Gulf region.
Adoption of Alternative Fuels and Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Energy transition initiatives within the cement sector reflect broader GCC sustainability commitments while addressing operational cost management imperatives. Alternative fuel adoption reduces dependence on conventional fossil fuels, lowering both carbon emissions and production costs. Alternative fuels and co-processing are expanding across kilns, with Yamama Cement and Arabian Cement introducing refuse-derived fuel at pilot scale aligned with Saudi Green Initiative goals. These pilot programs demonstrate technical feasibility and economic viability, paving the way for broader implementation.
Renewable energy integration represents another critical dimension of industry decarbonization efforts. Companies are increasing use of alternative energy sources, with examples including solar power advancement at cement plants and renewable energy projects supporting production facilities. As renewable energy costs continue declining and technologies mature, cement producers can increasingly rely on clean power sources, substantially reducing operational carbon footprints.
Energy efficiency improvements complement alternative fuel adoption, creating compounding benefits for environmental performance and cost management. The Cement and Concrete Breakthrough initiative strives to make near-zero-emission cement production established and growing in every region by 2030, requiring widespread adoption of innovative production processes. This global momentum toward decarbonization creates knowledge-sharing opportunities and technology transfer possibilities that benefit GCC producers seeking to accelerate their sustainability journeys.
Market Segmentation & Regional Insights:
The GCC cement market exhibits distinct segmentation patterns reflecting diverse applications, product specifications, and regional development priorities. Portland cement maintains market dominance based on its versatility, strength characteristics, and suitability for the region's demanding climate conditions. This traditional formulation serves as the foundation for most construction applications, from residential buildings to large-scale infrastructure projects. However, blended cement formulations incorporating supplementary cementitious materials are gaining traction, driven by sustainability considerations and performance optimization for specific applications.
End-use segmentation reveals the multifaceted nature of cement consumption across the Gulf. Residential construction constitutes a substantial demand stream, fueled by population growth, urbanization, and government housing initiatives. Commercial development, encompassing retail spaces, office complexes, and hospitality facilities, generates consistent consumption tied to economic diversification objectives. Infrastructure applications, including transportation networks, utilities, and civic facilities, represent the fastest-growing segment, reflecting massive public investment in modernization and expansion projects.
Regional dynamics within the GCC market highlight Saudi Arabia's predominant position. Saudi Arabia's ambitious Vision 2030 initiative has spurred significant investments in infrastructure and construction projects, with the country's rapidly growing population and increasing urbanization generating substantial residential and commercial construction needs. The United Arab Emirates follows as a significant market, characterized by advanced construction practices, high-value projects, and early adoption of sustainable building materials. Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, and Bahrain represent smaller but strategically important markets, each with unique development trajectories and cement consumption patterns shaped by national priorities and economic structures.
Geographic distribution of cement production capacity generally aligns with consumption patterns, though inter-regional trade remains significant. Proximity to major projects influences plant location decisions and capacity expansion strategies. Northern and Northwestern regions such as NEOM represent colossal undertakings significantly impacting the precast market long-term, with projects necessitating massive and sustained supply of advanced concrete solutions. This geographic concentration of mega-developments creates localized demand spikes that producers address through strategic capacity positioning, logistics optimization, and collaborative supply arrangements.
Forecast: Demand Drivers for Sustainable Growth:
Infrastructure Diversification and Vision 2030 Projects
Economic transformation initiatives across the GCC constitute the primary catalyst for sustained cement demand through the forecast horizon. Saudi Arabia's economy grew 3.9 percent year-on-year in the second quarter of 2025, driven by strong non-oil sector performance, with firms benefiting from ongoing project work and resilient domestic demand. This economic diversification trajectory creates sustained construction activity that extends far beyond current project pipelines, as new economic sectors require supporting infrastructure, facilities, and urban development.
The multi-phased nature of megaprojects ensures demand continuity over extended timeframes. Major developments proceed through distinct stages, each requiring specific cement applications and volumes. Initial phases focusing on foundational infrastructure give way to vertical construction, followed by finishing work and ancillary development. This sequential progression creates predictable demand patterns that support industry planning and investment.
Regional integration initiatives complement national development programs, generating cross-border infrastructure requirements. Transportation corridor improvements, utility interconnections, and coordinated industrial zone development create additional cement consumption beyond domestic project needs. These regional coordination efforts amplify overall demand while fostering market integration and operational efficiency across Gulf cement producers.
Rapid Urbanization & Housing Demand
Demographic trends fundamentally shape long-term cement consumption trajectories across the GCC region. Urbanization, with increasing population residing in cities as of 2025, is intensifying demand for housing and public infrastructure, all requiring significant cement volumes. Population concentration in urban centers necessitates continuous residential construction to accommodate growth, creating baseline demand independent of major project initiatives.
Government housing programs address demographic pressures while advancing social policy objectives. Affordable housing initiatives, homeownership encouragement schemes, and residential development projects generate substantial cement requirements. Municipal infrastructure and housing developments sustain base demand, with public housing schemes under the National Housing Company generating consistent consumption. These programmatic initiatives provide demand visibility and market stability, complementing larger but potentially more volatile project-based consumption.
Urban infrastructure supporting residential growth amplifies cement demand beyond housing units themselves. Schools, healthcare facilities, retail spaces, and community amenities accompany residential expansion, creating multiplier effects on construction materials consumption. Utility extensions, road networks, and public transportation serving new residential areas further contribute to sustained cement demand throughout urban expansion zones.
Growth of Industrial and Commercial Construction
Economic diversification drives industrial facility development across the Gulf, with cement-intensive manufacturing plants, logistics centers, and processing facilities becoming increasingly prominent. The Saudi Arabia concrete market is set to grow due to cost-efficient production advancements and government-funded construction projects, with power consumption accounting for considerable production costs. Industrial construction typically requires specialized cement formulations and substantial volumes, contributing disproportionately to overall consumption despite representing a smaller share of project counts.
Commercial development momentum reflects retail expansion, hospitality sector growth, and office space construction supporting diversifying economies. Tourism infrastructure development, particularly in Saudi Arabia and the UAE, drives hotel, resort, and entertainment venue construction requiring high-quality cement products. The marine and industrial construction sectors are expanding driven by new ports, offshore projects, and industrial cities, with cement suppliers adapting products for durability under harsh marine environments. These specialized applications command premium pricing while demonstrating the sector's technical sophistication and adaptability.
Mixed-use developments combining residential, commercial, and recreational functions represent an emerging trend with significant cement implications. These integrated communities require diverse cement applications across varying building types and construction methodologies. Smart city initiatives incorporating advanced technologies and sustainable design principles further complicate cement specifications while creating opportunities for innovative product development and value-added services.
Rising Investments in Smart Cities and Logistics Development
Digital infrastructure initiatives and smart city projects constitute a rapidly growing cement demand driver with substantial long-term potential. These developments integrate advanced technologies with physical infrastructure, requiring construction of data centers, fiber optic networks, sensor arrays, and integrated command facilities. The Saudi Arabian precast concrete market is continuously evolving driven by innovation and specific demands of the Kingdom's ambitious projects, with integration of smart technologies and digitalization becoming prominent. While individual smart city components may consume modest cement volumes, the comprehensive nature of these initiatives generates substantial aggregate demand.
Logistics sector expansion reflects the GCC's strategic positioning as a global trade hub and regional distribution center. Port developments, airport expansions, warehousing facilities, and intermodal transportation terminals require durable, high-performance concrete for demanding operational environments. Saudi Arabia is allocating more than $500 billion under Vision 2030 for projects including industrial hubs, with the UAE expanding logistics infrastructure. These investments create sustained cement consumption while establishing infrastructure foundations for continued economic growth.
Free trade zones, industrial parks, and special economic zones represent another dimension of logistics-related cement demand. These designated areas require comprehensive infrastructure development including access roads, utilities, and purpose-built facilities. As GCC nations compete to attract foreign investment and diversify their economic bases, proliferation of such zones generates predictable, sustained cement consumption that complements other demand drivers.
Conclusion:
The GCC cement market stands poised for continued expansion as regional economies pursue ambitious transformation agendas that fundamentally reshape urban landscapes and economic structures. Vision 2030 and parallel initiatives across Gulf nations have catalyzed unprecedented infrastructure investment, creating sustained demand for cement and construction materials that extends well beyond current project horizons. The confluence of megaproject development, rapid urbanization, industrial diversification, and demographic growth establishes a robust foundation for long-term sectoral growth.
Sustainability emergence as a defining industry priority represents both challenge and opportunity for GCC cement producers. The transition toward green cement, alternative fuels, and energy-efficient production processes requires substantial investment while creating competitive differentiation opportunities. Progressive companies that embrace decarbonization and technological innovation position themselves advantageously for evolving regulatory environments and market preferences. Industry collaboration with governments, research institutions, and value chain partners accelerates the sustainability transition while ensuring economic viability.
Strategic adaptation to changing market dynamics will determine individual producer success within the evolving GCC cement landscape. Capacity optimization, logistics efficiency, product innovation, and customer relationship management constitute critical success factors. The future of the Saudi cement industry hinges on its ability to adapt to rapid infrastructure build-out, strengthen environmental compliance, and participate in the circular economy while maintaining cost discipline. Producers that successfully navigate these imperatives while maintaining operational excellence and financial discipline will capture disproportionate value as the market matures.
Unlock Comprehensive Market Intelligence with IMARC Group:
At IMARC Group, we empower construction materials executives, investors, and policymakers with rigorous market intelligence that drives strategic advantage. Our cement industry research encompasses comprehensive demand analysis, competitive benchmarking, production capacity assessments, and forward-looking forecasts that illuminate market opportunities and risks.
Tailored Research Solutions
- Market Sizing and Forecasting: Quantify addressable markets, identify growth segments, and project future demand trajectories with confidence
- Competitive Intelligence: Analyze competitor strategies, capacity expansions, technology adoption patterns, and market positioning to inform strategic planning
- Regulatory and Policy Advisory: Navigate evolving environmental regulations, sustainability mandates, and policy frameworks affecting cement production and distribution
- Value Chain Analysis: Map supply chain dynamics, identify optimization opportunities, and assess raw material availability and pricing trends
- Technology Assessment: Evaluate emerging production technologies, alternative fuel viability, and decarbonization pathways relevant to your operations
Industry-Leading Expertise
Our multidisciplinary team combines deep cement industry knowledge with advanced analytical capabilities, delivering insights that transcend conventional market research. We leverage primary research, proprietary databases, and sophisticated modeling techniques to provide clarity amid market complexity. Whether you're planning capacity expansions, evaluating acquisition targets, or developing sustainability roadmaps, IMARC Group provides the intelligence foundation for confident decision-making.
Partner with Excellence
Join leading cement producers, construction firms, investors, and government agencies who rely on IMARC Group for market intelligence that drives results. Our commitment to analytical rigor, client service, and actionable insights has established us as the preferred research partner for stakeholders shaping the future of the construction materials industry.
Contact IMARC Group today to explore how our cement market research capabilities can advance your strategic objectives and accelerate your growth trajectory in this dynamic, high-opportunity sector.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104
.webp)










